Spam bots submitted over 99 billion junk form entries across the web in 2024. Your site caught some of that traffic, guaranteed. The best tactics for form spam prevention combine…
Table of Contents
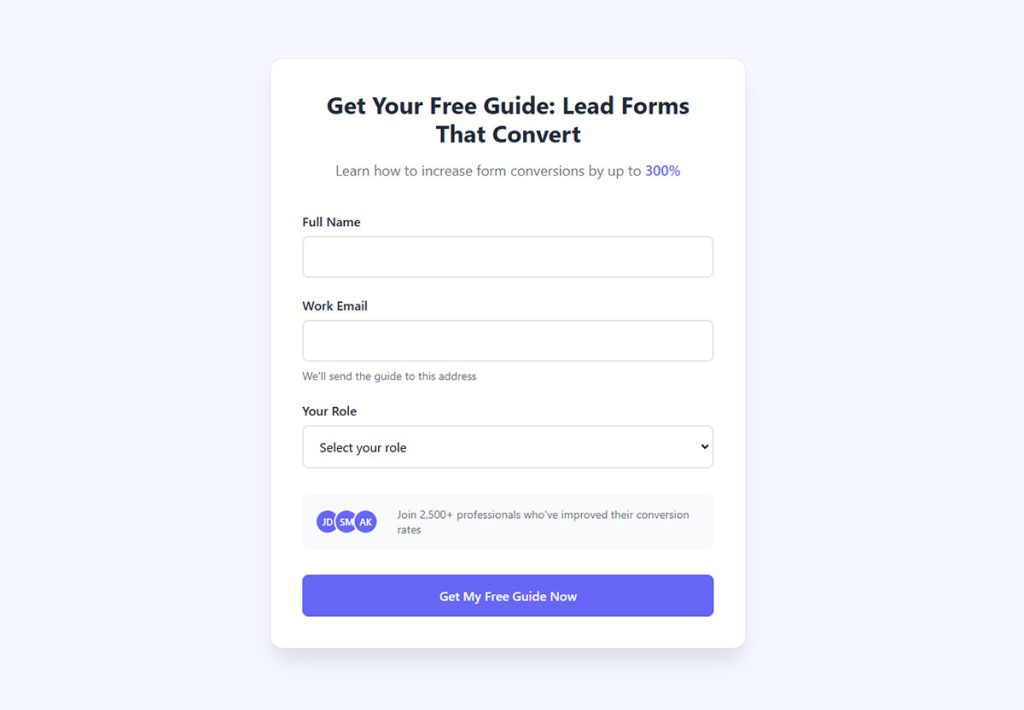
Your website gets traffic, but visitors leave without giving you their contact information. Every anonymous visitor represents lost revenue potential.
Learning how to create lead capture forms that convert changes this dynamic completely. Well-designed forms transform passive browsers into qualified prospects you can nurture into customers.
This guide covers form design principles, placement strategies, technical implementation, and optimization tactics that boost conversion rates. You’ll discover which form fields increase submissions, how mobile optimization impacts performance, and what compliance requirements protect your business.
The difference between 3% and 25% conversion rates often comes down to these specific elements.
What is a Lead Capture Form?
A lead capture form collects visitor information (name, email, phone) in exchange for something valuable. They turn anonymous website traffic into contacts you can market to.
Think of them as digital business card collectors. Every submission gives you permission to follow up, nurture, and eventually convert that person into a customer.
Core Elements of High-Converting Forms
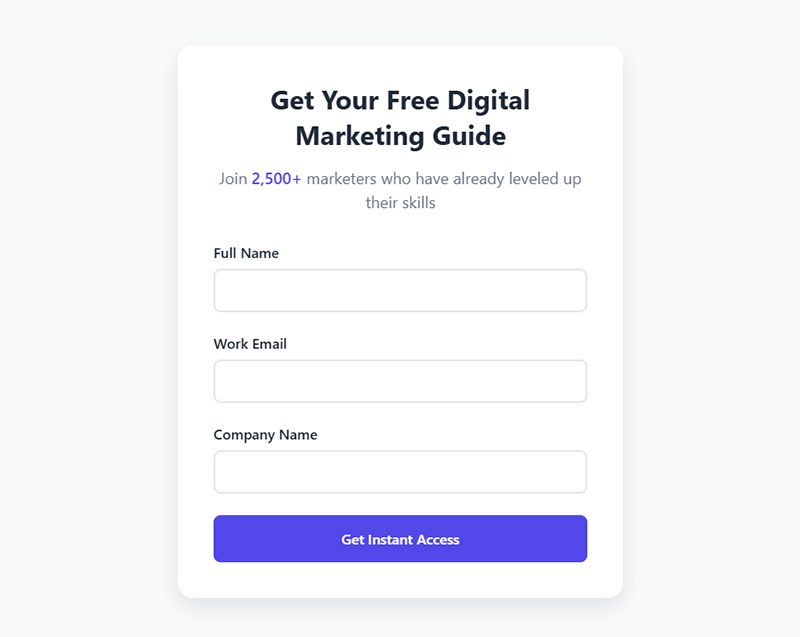
The difference between a 2% conversion rate and a 25% conversion rate often comes down to getting these fundamentals right.
Form Fields That Matter
Number of Fields
Three to five fields work best for top-of-funnel offers. Seven to ten fields make sense when you need qualification data for high-ticket services.
Every additional field drops your completion rate by roughly 5-10%. Remove anything you can ask later in the relationship.
Field Types and Labels
Text inputs handle most use cases. Dropdowns work when you have 3-8 preset options. Radio buttons beat checkboxes for single selections.
Labels sit above fields, not beside them (this improves mobile forms completion by 15-20%). Placeholder text shouldn’t replace labels.
Different types of forms serve different purposes. Match your field selection to what you’re actually offering.
Visual Design Components
Form Layout
Single-column layouts convert better than multi-column on almost every test. Your eye travels down naturally, not across.
Multi-step forms work when you need 8+ fields but don’t want to scare people away with a wall of inputs. Break it into digestible chunks.
CTA Button Design
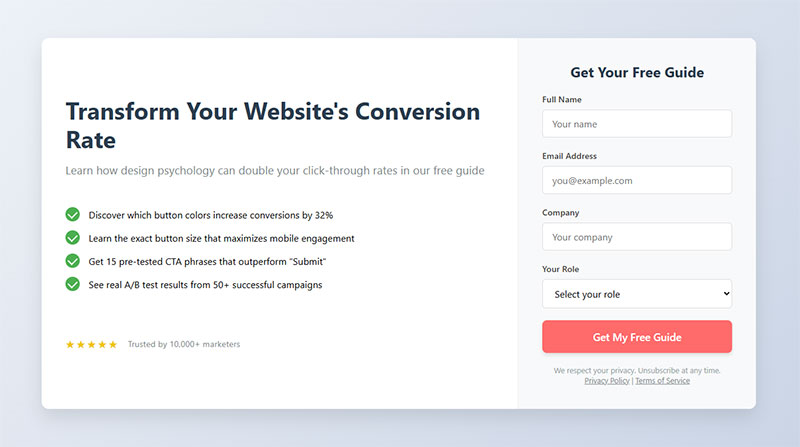
Button size matters. Minimum 44×44 pixels for touch targets (mobile requirement). Make it the most visually prominent element on the page.
Color psychology plays a role, but contrast matters more. Your button should pop against the background. Orange and green consistently perform well across industries, but test what works for your audience.
Button text should be specific. “Get My Free Guide” beats “Submit” every time.
Psychological Triggers for Form Completion
Trust Signals
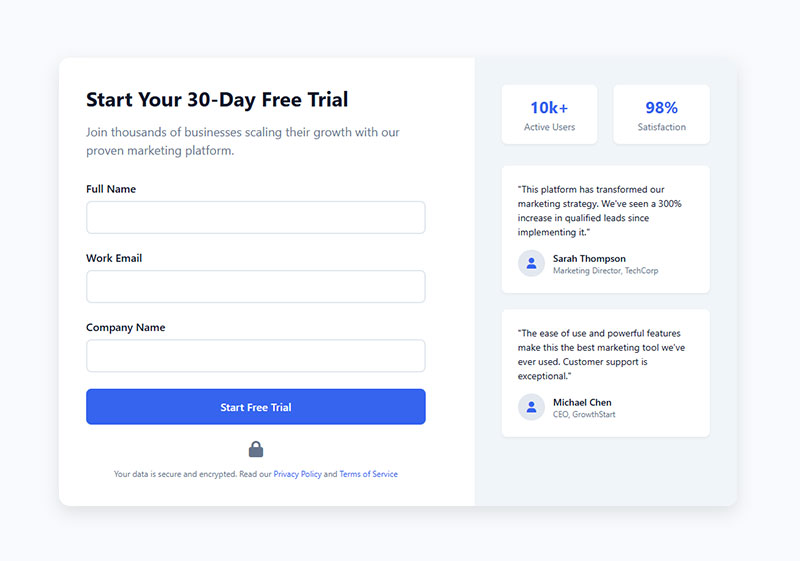
Privacy statements below your form increase conversions by 20-30%. People worry about spam.
Security badges (SSL certificates, privacy seals) reduce anxiety. Social proof (submission counts, testimonials) creates FOMO.
Look at successful lead generation form designs. They all include trust elements prominently.
Value Proposition Clarity
State exactly what someone gets and when they’ll get it. “Download your free checklist instantly” beats vague promises.
The exchange needs to feel fair. Asking for a phone number to download a PDF? That’s a hard sell unless your content is genuinely premium.
Benefits should be visible without scrolling. If visitors can’t see the value, they won’t fill out the form.
Friction Reduction
Autofill saves people time. Modern browsers handle this automatically if you use proper form fields and attributes.
Smart defaults pre-select the most common option. Country dropdowns should default to your primary audience’s location.
Inline validation shows errors immediately, not after submission. Real-time feedback prevents frustration and abandonment.
Form Placement Strategies
Location determines visibility. Visibility drives submissions.
Page Locations
Homepage Forms
Homepage lead capture forms work for businesses with one clear offer. They fail when you have multiple services or audience segments.
Above-the-fold placement captures hot traffic. Below-the-fold works when you need to build context first.
Landing Page Forms

Dedicated landing pages convert 5-10x better than general pages. One page, one goal, one form.
Remove navigation. Kill sidebar distractions. Every element should guide eyes toward form completion.
Check these landing page forms principles before building your next campaign page.
Blog Sidebar Forms
Content upgrades relevant to the article topic convert at 10-25%. Generic newsletter signup boxes hover around 1-3%.
Sticky sidebars keep forms visible as readers scroll. But mobile needs different treatment since sidebars disappear.
Exit-Intent Popups
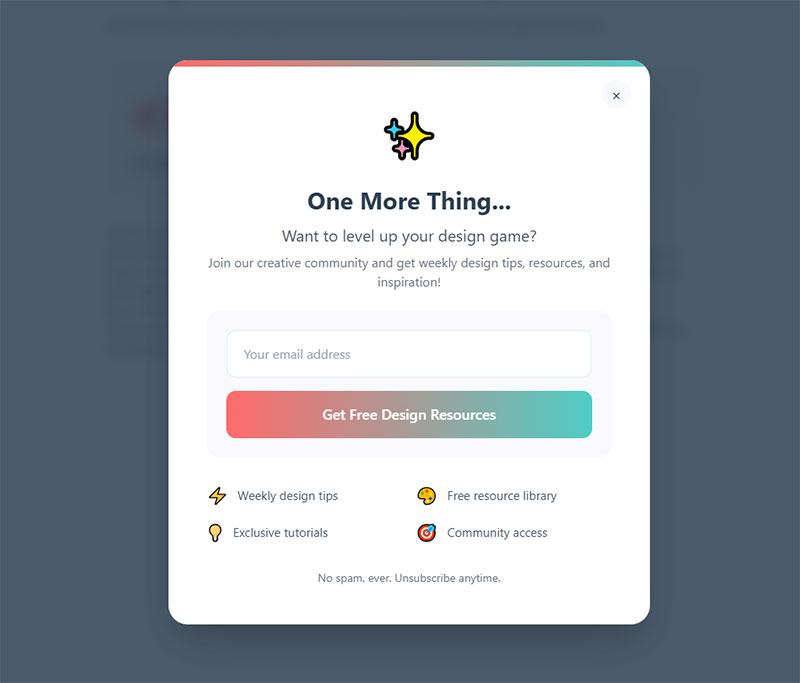
Exit-intent forms trigger when mouse movement indicates someone’s about to leave. They capture 2-4% of otherwise lost traffic.
The offer needs to match abandonment intent. Someone leaving a pricing page might respond to a discount. Someone leaving a blog post might want related content.
Timing matters more than most people think.
Timing Mechanisms
Scroll-Triggered Forms
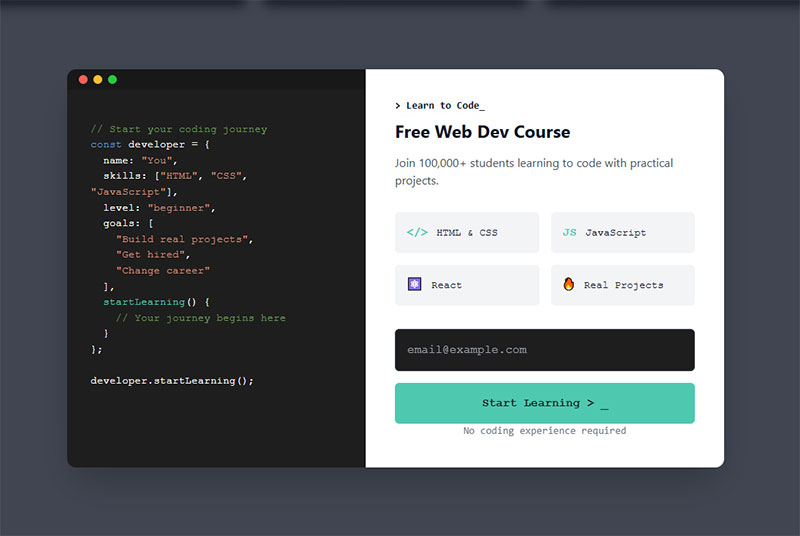
Forms appearing at 50-70% scroll depth catch engaged readers. They’ve invested time, shown interest, and might be ready to convert.
Too early feels pushy. Too late misses the engagement window.
Time-Delayed Forms
30-60 second delays work for content-heavy pages. Immediate popups annoy visitors who haven’t even read your headline yet.
Test different delays for different page types. Blog posts need longer delays than landing page forms.
Behavior-Triggered Forms
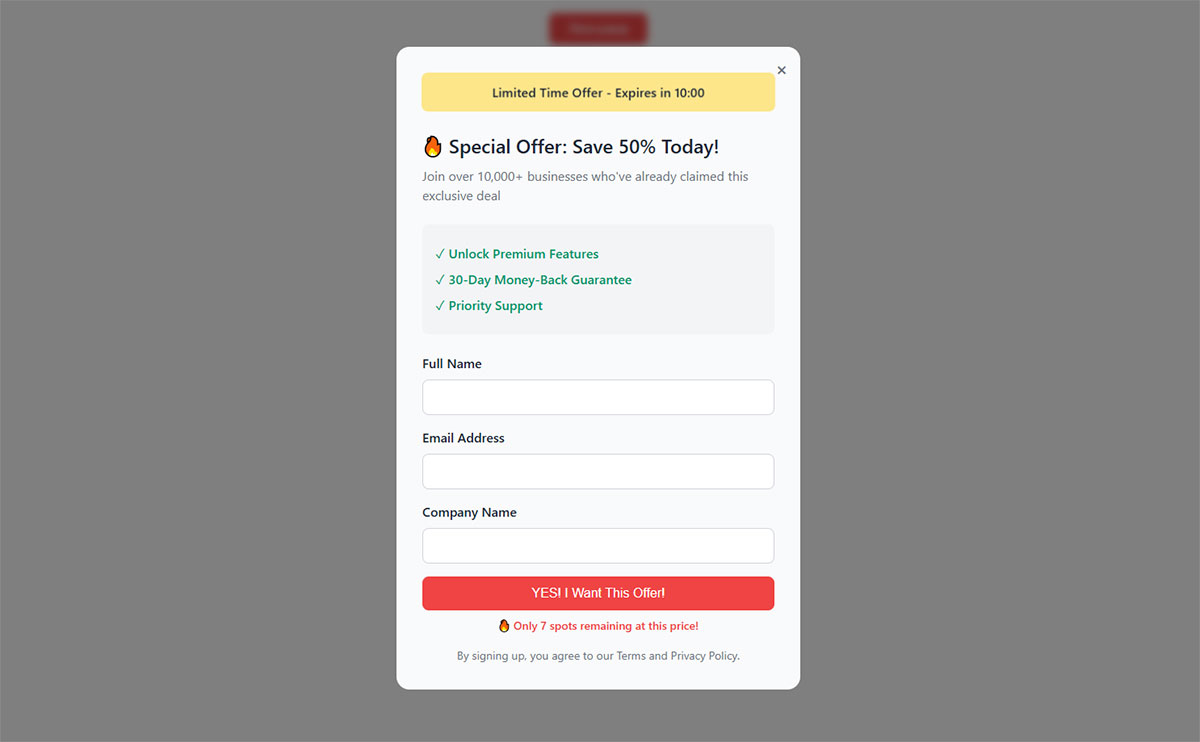
Click-triggered forms appear after specific actions (watching a video, clicking a demo button, viewing multiple pages). They target hot prospects who’ve demonstrated intent.
Return visitor detection lets you show different forms to people who’ve been there before. First-time visitors get awareness offers, returning visitors get conversion offers.
Technical Implementation
Bad code kills good design. Forms that don’t work don’t convert.
HTML Structure
Semantic Form Markup
Proper HTML tags (form, label, input, button) help browsers understand structure. This enables autofill, password managers, and accessibility features.
Input types matter. type="email" triggers email keyboards on mobile. type="tel" shows number pads.
Name attributes should match standard conventions. Use “email” not “email_address” or “user_email” for maximum autofill compatibility.
Accessibility Attributes
ARIA labels help screen readers. Required attributes tell users which fields they must complete.
Error messages need to be programmatically associated with inputs. Visual red borders aren’t enough for vision-impaired users.
Following form accessibility standards isn’t optional if you want to reach everyone.
Validation Rules
Client-side validation provides instant feedback. Server-side validation prevents malicious submissions.
Email format checking should accept all valid email patterns (including plus addressing and international domains). Phone validation should handle different country formats.
Integration Points
CRM Connections
Forms feed data into Salesforce, HubSpot, or whatever CRM you use. API connections beat manual exports every time.
Field mapping needs to be exact. Your form’s “Company Name” must match your CRM’s company field, or data ends up in the wrong place.
Duplicate detection prevents the same lead from creating multiple records. Check email addresses before creating new contacts.
Email Marketing Platforms
Mailchimp, ConvertKit, and ActiveCampaign all offer direct integrations. Form submissions trigger welcome sequences automatically.
Tag new subscribers based on which form they completed. Someone downloading a pricing guide needs different emails than someone requesting a demo.
Analytics Tracking
Google Analytics needs to track form views, interactions, and completions as events. Standard pageview tracking misses crucial conversion data.
Set up goals for each form. Track submission sources. Know which traffic channels actually generate leads (not just visits).
Conversion funnels show where people drop off. Maybe they’re filling out three fields then bouncing. Fix that specific friction point.
Performance Optimization
Load Time Impact
Heavy form plugins slow page speed. Every second of delay costs you 7% of conversions.
Lazy load forms below the fold. Critical above-the-fold forms should render immediately.
Mobile Responsiveness
Thumb-friendly tap targets prevent fat-finger errors. Input fields need adequate spacing on small screens.
Mobile forms account for 60-70% of traffic on most sites. Desktop-only optimization leaves money on the table.
Vertical layouts work universally. Side-by-side fields create problems on narrow screens.
Cross-Browser Compatibility
Test in Chrome, Safari, Firefox, and Edge minimum. Form behavior varies wildly between browsers.
Date pickers, file uploads, and select dropdowns all have browser-specific quirks. Polyfills handle older browser versions.
Conversion Rate Optimization Tactics
Testing reveals truth. Opinions lose to data.
A/B Testing Variables
Headline Variations
Question headlines (“Want More Leads?”) often outperform statement headlines (“Get More Leads”). But not always—test your audience.
Benefit-driven headlines beat feature-driven headlines. “Double Your Email List in 30 Days” works better than “Advanced Email Marketing Guide.”
Field Combinations
Test removing fields one at a time. Start with the least necessary field and measure impact.
Sometimes adding a field (like job title for B2B) improves lead quality enough to justify lower volume. Quality vs. quantity trade-offs depend on your sales process.
Progressive profiling asks different questions on repeat visits. First visit: name and email. Second visit: company and role.
Button Text Options
First-person button copy (“Get My Guide”) converts better than second-person (“Get Your Guide”) in most tests. Makes it feel more personal.
Action verbs drive clicks. “Download,” “Send,” “Start,” “Join” all perform well. Avoid passive language.
Urgency works if it’s genuine. “Get Instant Access” beats “Submit” because it promises immediate value.
Color Schemes
High-contrast buttons get more clicks. This isn’t about picking the “best” color, it’s about visual hierarchy.
Brand colors matter less than conversion colors. Your form isn’t a branding exercise.
Red creates urgency. Green implies “go” or “safe.” Orange balances both. Test them all rather than guessing.
Data-Driven Improvements
Conversion Metrics
Track form view-to-submission rate. 10-25% is decent for most lead gen forms. Under 5% means something’s broken.
Time-to-complete reveals friction. Forms taking over 90 seconds to fill out probably need simplification.
Device-specific conversion rates show mobile problems. If mobile converts at half your desktop rate, you have UX issues.
Drop-Off Analysis
Field-level analytics show where people abandon. If 40% of people click the first field but don’t submit, something between start and finish creates friction.
Heatmaps reveal which fields get the most corrections. Repeated corrections indicate confusing labels or validation issues.
Session recordings show real user behavior. Watch five people struggle with your form and you’ll find problems analytics miss.
Industry-Specific Form Strategies
What works for SaaS fails for healthcare. Context determines design.
B2B Lead Capture
Company size and revenue fields help sales teams prioritize. Budget qualifiers prevent wasting time on unqualified prospects.
Job titles matter in B2B. “Marketing Manager” gets different follow-up than “CEO.”
Generating B2B leads requires different tactics than consumer marketing. Longer forms work because purchase decisions involve multiple stakeholders.
E-commerce Forms
Guest checkout always. Forced account creation kills 25-30% of purchases.
Email capture at cart stage preserves abandonment recovery options. You can still send reminder emails without requiring full registration.
Post-purchase feedback forms gather testimonials and improve products. Just don’t ask immediately after checkout.
Service-Based Business Forms
Consultation booking needs calendar integration. Picking a specific time converts better than “we’ll call you.”
Service selection dropdowns qualify leads automatically. Someone requesting enterprise consulting needs different handling than basic package inquiries.
Lead generation for coaches differs from lead generation for contractors in field requirements and qualification questions.
Compliance and Legal Requirements
Breaking privacy laws costs more than lost conversions.
GDPR Considerations
Consent Mechanisms
Pre-checked boxes don’t count as consent under GDPR. Users must actively opt in.
Separate checkboxes for different purposes (marketing emails vs. account updates). Bundled consent isn’t valid.
Creating GDPR compliant forms protects you legally and builds trust with European visitors.
Data Processing Notices
Tell people what data you collect, why you collect it, and how long you keep it. Vague language doesn’t meet compliance standards.
Cookie consent and form consent are separate. Both need explicit agreements.
Opt-In Requirements
Double opt-in reduces spam complaints and improves deliverability. New subscribers confirm their email before joining your list.
Single opt-in converts better but attracts more fake submissions. Choose based on your lead quality needs.
Privacy Policy Integration
Link Placement
Privacy policy links belong near the submit button. “By submitting, you agree to our Privacy Policy” language works.
Making people scroll to find your privacy policy creates unnecessary friction. Keep it visible but not intrusive.
Transparency Requirements
State whether you share data with third parties. List email service providers, CRM systems, and analytics tools.
Data retention periods matter. How long do you keep contact information? What happens when someone requests deletion?
Data Usage Disclosure
Be specific about email frequency. “Weekly newsletter” sets clear expectations; “occasional updates” doesn’t.
Explain how you protect personal information. SSL encryption, secure storage, limited access—these details build confidence.
Mobile Form Optimization
Mobile traffic dominates. Your forms better work flawlessly on small screens.
Touch-Friendly Design
Input Size Specifications
Minimum 44×44 pixel tap targets prevent mis-taps. Fingers aren’t as precise as mouse cursors.
Field height matters more on mobile. 40-50 pixel tall inputs work better than desktop-standard 32 pixels.
Spacing between fields reduces errors. 8-16 pixels of vertical space prevents accidentally tapping the wrong field.
Spacing Requirements
Adequate padding around clickable elements improves accuracy. Cramped forms frustrate users.
Button spacing needs extra attention. Submit buttons should sit 30+ pixels below the last input field.
Keyboard Optimization
Input types trigger appropriate keyboards. type="email" shows @ symbol prominently, type="tel" brings up number pad.
Autocapitalize and autocorrect attributes should match field types. Names get autocapitalize, emails don’t.
Mobile-Specific Features
Click-to-Call Buttons
Phone number fields can link directly to device dialers. One tap starts the call.
“Call Now” CTAs work better than forms for urgent service requests. Someone with a burst pipe doesn’t want to fill out fields.
Location Detection
Auto-detecting city and state saves typing. Requires permission but worth asking for location-dependent services.
“Near me” searches drive local business traffic. Capturing location data improves targeting.
Camera Access for Uploads
Mobile file uploads should allow camera capture. Insurance claims, project photos, document scans all benefit from direct camera access.
WordPress form with file upload capabilities handle photo submissions from mobile devices automatically.
Common Form Mistakes
Most conversion problems come from these repeated errors.
Overcomplication
Too Many Fields
Every field costs conversions. Asking for middle name, suffix, fax number—all unnecessary friction.
“Nice to have” information isn’t worth losing 30% of submissions. Ask only what you absolutely need.
Unclear Instructions
Password requirements need to be visible before people type. “Must include uppercase, number, and special character” shown after a failed attempt frustrates users.
Format requirements (phone number dashes, date formatting) should appear as placeholder text or helper text.
Complex Validation Rules
Rejecting valid emails because they contain plus signs or hyphens loses real leads. Email regex should accept all RFC-compliant formats.
Overly strict password rules reduce security (people write them down) and increase abandonment.
Poor User Experience
Slow Loading Forms
Third-party form embeds often load slowly. Self-hosted solutions with optimized code perform better.
Heavy JavaScript frameworks add unnecessary bulk. Simple forms don’t need React.
Missing Error Messages
Generic “Please fix errors” messages don’t help. Highlight the specific field and explain what’s wrong.
Form error message design should be obvious but not aggressive. Red text works, angry modal dialogs don’t.
Unclear Success States
Users need confirmation their submission worked. A form submission confirmation message or redirect to a thank-you page prevents duplicate submissions.
Email confirmations provide backup proof. Send immediately, include submission details.
Form Analytics and Tracking
You can’t improve what you don’t measure.
Key Metrics
Form Views
How many people see your form? Low view counts indicate traffic or visibility problems, not form problems.
Unique views vs. total views show whether the same visitors keep returning without converting.
Interaction Rate
Percentage of viewers who click into any field. 50-70% interaction rate is normal for visible forms.
Low interaction suggests value proposition failure. People see the form but don’t care enough to start.
Completion Rate
Submissions divided by interactions. 70-80% completion means your form works well once people start.
Under 50% completion indicates UX issues, trust problems, or field-level friction.
Time to Complete
30-60 seconds for simple lead gen forms. Over 2 minutes suggests complexity issues.
Outliers matter. If median time is 45 seconds but some people take 10 minutes, find out what causes the delay.
Field-Level Analytics
Which field has the highest abandonment? That’s your problem field.
Correction frequency shows confusing labels. If 40% of people edit the “Company” field multiple times, your label or validation is unclear.
Tracking Implementation
Event Tracking Setup
Google Analytics events should fire on form view, first interaction, field completion, and submission.
Custom dimensions capture form ID, page URL, and traffic source. This data reveals which acquisition channels generate quality leads.
Goal Configuration
Each form should map to a specific conversion goal. Assign monetary value based on lead-to-customer conversion rates.
Funnel visualization needs proper event sequencing. Track the path from page load to submission completion.
Funnel Visualization
Identify exact drop-off points. Losing 50% between field three and four? Fix field four.
Segment by device, traffic source, and new vs. returning visitors. Mobile drop-off patterns differ from desktop.
Advanced Form Features
These tactics separate basic forms from conversion machines.
Progressive Profiling
Gradual Information Gathering
First visit asks for name and email. Second visit asks for company and role. Third visit asks about budget and timeline.
This strategy maintains low initial friction while building complete profiles over time. Works best with returning website visitors.
Smart Field Display
Hide fields that don’t apply based on previous answers. Conditional logic shows relevant questions only.
B2B visitors see company fields; B2C visitors don’t. Geography-based field display matches local requirements.
Returning Visitor Recognition
Cookie tracking identifies repeat visitors. Pre-fill known information so they don’t retype everything.
Existing customers get different forms than new prospects. Personalization improves conversion and user experience.
Conditional Logic
Dynamic Field Display
Service selection determines which additional fields appear. Legal consultation forms differ from tax prep forms.
Budget ranges trigger appropriate follow-up questions. Someone selecting “$50k+” budget sees different options than “$5k or less.”
Skip Logic Implementation
“Not applicable” answers skip entire sections. Keeps forms lean for each respondent while gathering diverse data across submissions.
Branch logic creates personalized paths. Each user sees only relevant questions.
Personalized Paths
Industry selection customizes all subsequent questions. Healthcare providers see HIPAA compliance questions; e-commerce businesses see platform integration options.
Multi-Step Forms
Progress Indicators
Show “Step 2 of 4” or visual progress bars. Completed steps should be clearly marked.
Progress indicators reduce abandonment by managing expectations. People complete tasks when they know how much remains.
Save and Resume Functionality
Long forms benefit from save-for-later options. Email a unique link to resume incomplete submissions.
Especially valuable for WordPress event registration form use cases and complex applications.
Step Optimization
Each step should take 15-30 seconds maximum. Longer steps feel overwhelming.
Most critical information first. If someone abandons halfway, you still captured basic contact details.
Back buttons let people correct earlier answers without losing progress. Forced forward-only navigation frustrates users.
FAQ on Create Lead Capture Forms That Convert
What’s the ideal number of form fields?
Three to five fields for top-of-funnel offers, seven to ten for qualified B2B leads. Every additional field drops completion rate by 5-10%. Remove anything you can ask later in your nurturing sequence.
Should I use single-step or multi-step forms?
Multi-step forms or single-step forms depends on field count. Under six fields, single-step works best. Over eight fields, breaking into multiple steps improves completion rates by reducing visual overwhelm.
Where should I place my lead capture form?
Above-the-fold on landing pages, embedded in relevant blog content, and triggered via scroll or exit-intent on high-traffic pages. Match placement to visitor intent and page context for best results.
How do I reduce form abandonment?
Minimize required fields, add autofill capabilities, show inline validation, include trust signals, and ensure mobile optimization. Improving form abandonment rate requires addressing friction at every step.
What makes a CTA button convert better?
High-contrast colors, minimum 44×44 pixel size, specific action-oriented text (“Get My Guide” not “Submit”), and prominent placement. Button copy should emphasize immediate value rather than generic actions.
Do I need GDPR compliance for my forms?
Yes, if you collect data from EU visitors. Requires unchecked opt-in boxes, clear data usage disclosure, and easy unsubscribe options. Non-compliance brings fines up to €20 million or 4% of revenue.
How can I A/B test my forms effectively?
Test one variable at a time: headline, field count, button color, or form length. Run tests until reaching statistical significance (usually 100+ conversions per variation). Track conversion rate, lead quality, and revenue impact.
What’s the best way to handle form errors?
Show errors inline as users complete fields, not after submission. Use specific error messages (“Email format invalid” not “Error in field”), highlight problem fields in red, and preserve entered data.
Should I use popup forms or inline forms?
Inline forms or popup forms both work depending on context. Popups capture exit traffic and urgency-driven offers. Inline forms work for content-driven conversions and less aggressive tactics.
How do I optimize forms for mobile devices?
Use single-column layouts, 44×44 pixel tap targets, appropriate input types (email, tel, number), vertical spacing between fields, and thumb-friendly button placement. Mobile accounts for 60-70% of traffic on most sites.
Conclusion
The ability to create lead capture forms that convert separates businesses that grow from those that struggle. Form design, placement strategy, and technical optimization all contribute to conversion performance.
Start by reducing form fields to essentials only. Add trust signals and mobile-friendly design. Test button colors, headlines, and field combinations systematically.
Track form analytics religiously. Measure completion rates, identify drop-off points, and fix friction immediately.
Progressive profiling and conditional logic help gather detailed information without overwhelming visitors. Compliance with GDPR and privacy regulations protects your business while building subscriber trust.
Small improvements compound over time. A 5% conversion lift today means hundreds of additional qualified prospects next quarter. Implement these tactics and watch your lead generation results improve.