Most buttons on the internet get ignored. The copy is vague, the placement is off, and the visitor leaves without doing anything. The difference between a page that converts at…
Table of Contents
Most forms fail before anyone clicks submit. Too many fields, confusing labels, broken validation on mobile. The result is always the same: users leave.
The difference between a form that converts at 3% and one that converts at 25% often comes down to layout decisions, field count, and how errors are handled.
Not guesswork.
Actual form design choices backed by UX research and real-world testing from teams at Baymard Institute, Nielsen Norman Group, and companies like Shopify and Airbnb.
This article breaks down proven form design examples across registration pages, checkout flows, contact pages, lead generation, and survey forms. Each example includes what works, what doesn’t, and why.
Form Design Examples
| Form Type | Primary Purpose | User Intent Context | Conversion Stage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contact Forms | Enable direct communication and inquiry submission | Information-seeking, support requests, business inquiries | Consideration to Decision |
| Registration Forms | Create user accounts and capture member data | Service access, community joining, platform onboarding | Decision to Action |
| Login Forms | Authenticate existing users and provide access | Return user authentication, secure area access | Retention & Engagement |
| Survey Forms | Collect feedback, opinions, and research data | Opinion sharing, research participation, feedback provision | Post-Purchase Engagement |
| Newsletter Signup | Build email lists and enable content distribution | Content consumption, updates subscription, lead nurturing | Awareness to Consideration |
| Checkout Forms | Process transactions and capture payment data | Purchase completion, payment processing, order finalization | Decision to Purchase |
| Job Application | Collect candidate information and qualifications | Career advancement, employment seeking, skills presentation | Interest to Application |
| Feedback Forms | Gather user experience insights and improvement data | Experience evaluation, service improvement, satisfaction measurement | Post-Interaction Analysis |
| Search Forms | Enable content discovery and information retrieval | Information discovery, content navigation, query processing | Awareness & Exploration |
| Multi-step Forms | Break complex data collection into manageable segments | Progressive disclosure, reduced cognitive load, guided completion | Variable (Context-Dependent) |
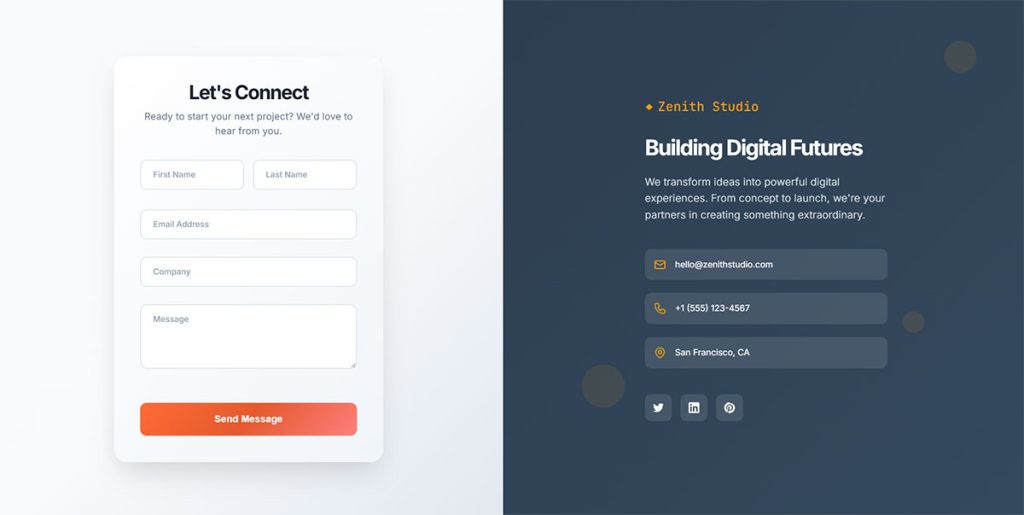
Contact Forms
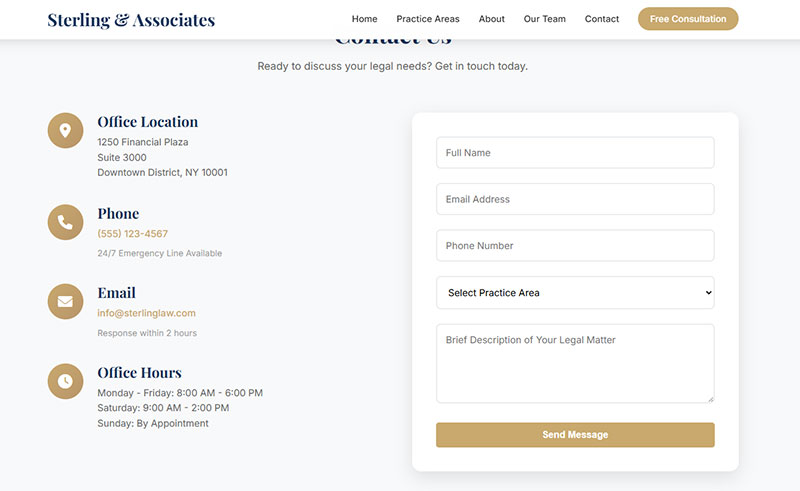
Contact forms serve as the primary communication bridge between businesses and website visitors. They handle customer inquiries, support requests, and lead generation activities.
Performance Metrics & Usage
- Conversion Rate: Contact forms convert at only 9.09% on average
- Completion Time: Most contacts complete submission within 2-3 minutes
- Field Count: Optimal forms contain 3-4 input fields maximum
- Mobile Usage: 45% of submissions occur on mobile devices
Core Components & Design Elements
Contact forms utilize essential field types including name inputs, email addresses, message text areas, and submit buttons. Modern implementations feature responsive layouts with single-column designs for mobile optimization.
Advanced contact forms integrate spam protection through CAPTCHA systems and honeypot fields. Form validation provides real-time feedback on field requirements and formatting errors.
Technology Integration & Security
Contact forms connect with email services, customer relationship management systems, and marketing automation platforms. Security protocols include SSL encryption, spam filtering, and form security measures.
Integration capabilities extend to popular platforms through API connections and webhook configurations. Database storage options range from cloud services to local server installations.
Implementation Best Practices
Field placement follows logical sequences with required fields clearly marked. Submit button text uses action-oriented language like “Send Message” instead of generic “Submit” commands.
Trust signals appear near form areas including privacy policy links and security badges. Error message design provides clear guidance without frustrating user experiences.
Registration Forms
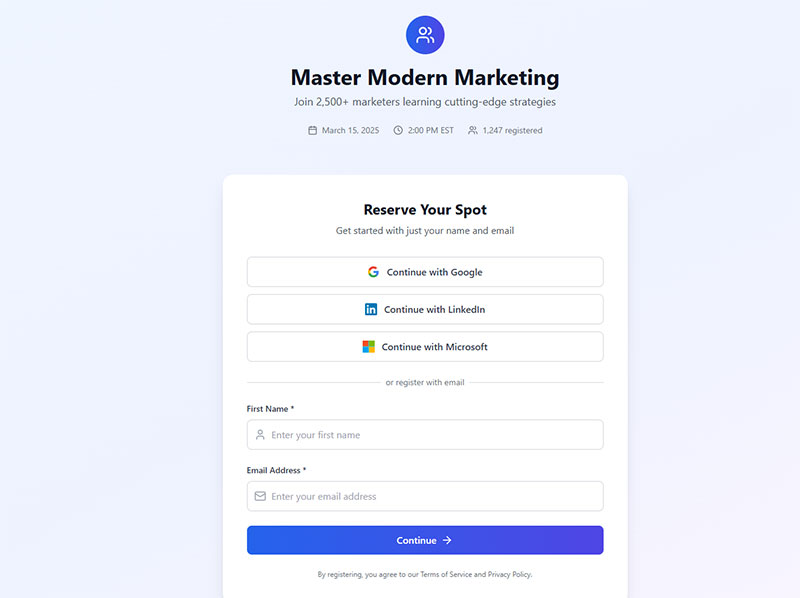
User registration forms create new accounts and capture essential user information for platform access. They balance data collection needs with conversion optimization requirements.
Performance Analysis & Metrics
- Completion Rate: 63.37% of started registration forms finish successfully
- Average Fields: Registration forms typically contain 6-8 required fields
- Completion Time: Users spend approximately 1 minute 35 seconds completing registration
- Industry Variation: B2B services achieve 2.5% conversion rates versus 0.8% for B2C platforms
Essential Form Architecture
Registration forms collect usernames, email addresses, passwords, and basic profile information. Progressive disclosure techniques reveal additional fields based on user selections and account types.
Password strength indicators guide users toward secure password creation. Email verification workflows confirm account authenticity through confirmation links and double opt-in processes.
User Experience Optimization
Single sign-on options through Google, Facebook, and LinkedIn reduce form friction by 8.2 percentage points. Social authentication eliminates password requirements and speeds account creation.
Multi-step registration breaks complex forms into digestible sections. Progress indicators show completion status and remaining steps to reduce abandonment rates.
Integration Capabilities
Registration systems connect with user authentication services, email marketing platforms, and customer databases. API integrations synchronize user data across multiple business applications.
Automated welcome email sequences engage new registrants with onboarding content and platform tutorials.
Login Forms
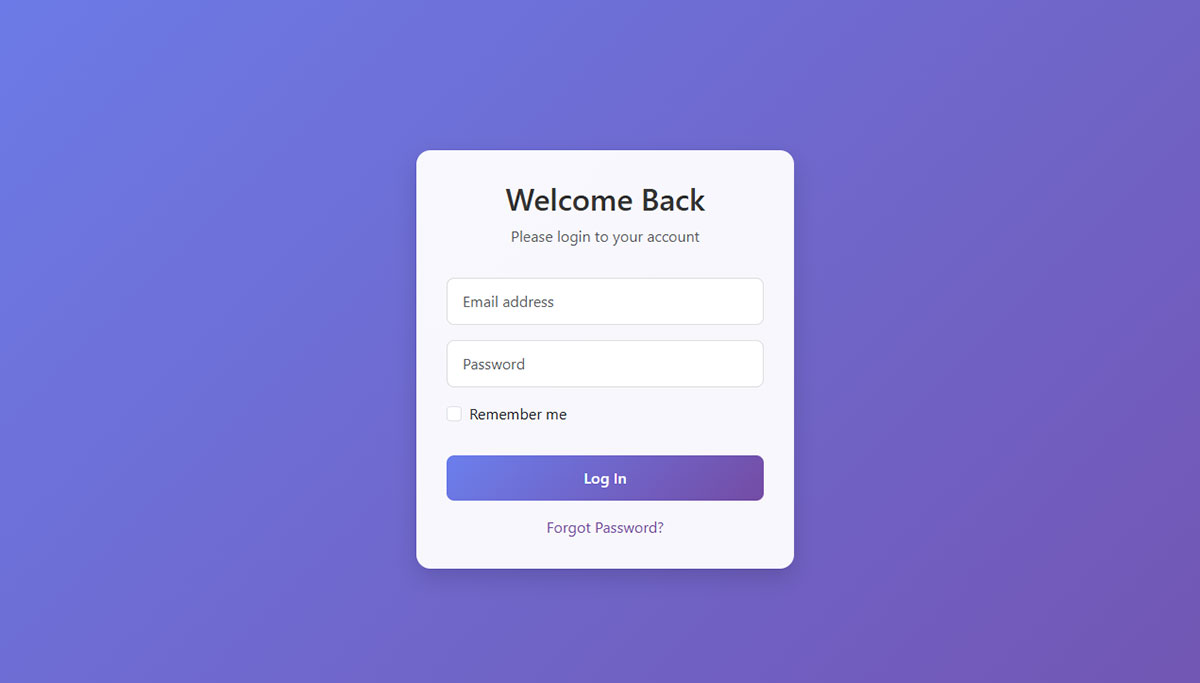
Login forms authenticate existing users and provide secure access to protected areas. They prioritize security while maintaining user convenience.
Security & Performance Standards
- Authentication Methods: Password, two-factor authentication, biometric options
- Session Management: Secure token generation and expiration handling
- Failure Protection: Account lockout after multiple failed attempts
- Remember Me: Optional persistent login functionality
Design Principles & Layout
Login forms use minimal field requirements with username/email and password inputs. Forgot password links provide account recovery options without customer service intervention.
Visual hierarchy emphasizes primary login action while secondary options remain accessible. Error messages specify whether username or password caused authentication failure.
Advanced Authentication Features
Two-factor authentication adds security layers through SMS codes, authenticator apps, and email confirmations. Biometric authentication supports fingerprint and facial recognition on compatible devices.
Single sign-on integration allows login through existing accounts from Google, Microsoft, and social media platforms.
Technical Implementation
Login forms implement HTTPS encryption for data transmission security. Session tokens expire after predetermined timeframes to prevent unauthorized access.
Rate limiting prevents brute force attacks while CAPTCHA challenges block automated login attempts.
Survey Forms
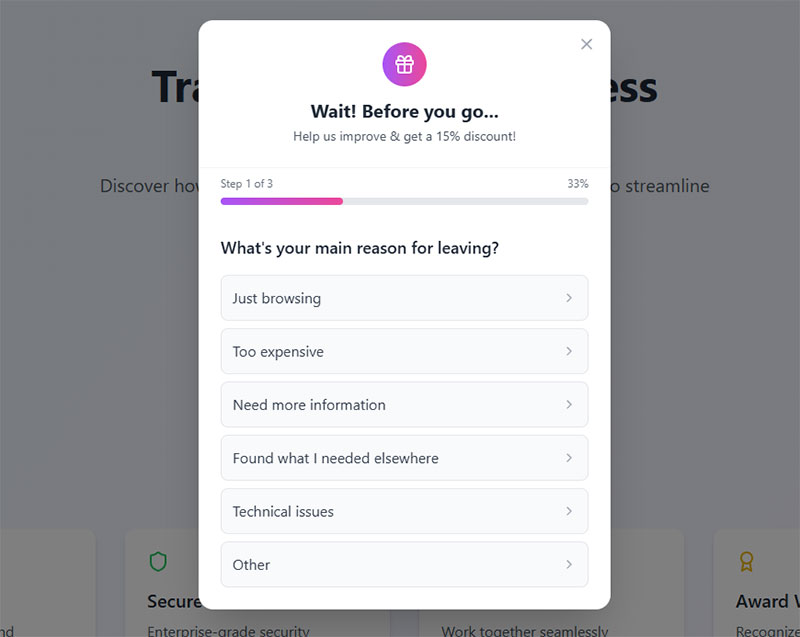
Survey forms collect structured feedback, market research data, and customer satisfaction metrics. They transform qualitative insights into actionable business intelligence.
Response Patterns & Engagement
- Completion Rates: Survey completion varies from 20-80% based on length and incentives
- Question Types: Multiple choice, rating scales, open-ended responses, matrix questions
- Optimal Length: 5-10 questions maintain highest completion rates
- Mobile Optimization: Mobile-friendly designs increase response rates by 30%
Question Design & Structure
Effective surveys use logical question sequences that flow from general to specific topics. Conditional logic shows relevant questions based on previous responses.
Rating scales provide quantitative feedback through Likert scales and numerical ratings. Open-ended questions capture detailed qualitative insights that structured questions miss.
Data Collection & Analysis
Survey platforms export data in CSV, Excel, and database formats for analysis. Real-time reporting shows response trends and completion statistics.
Integration with analytics tools enables advanced data visualization and statistical analysis of survey results.
Best Practices & Optimization
Pre-testing surveys with small groups identifies confusing questions and technical issues. Incentive programs increase response rates through discounts, prizes, and exclusive content.
Progress bars show completion status while estimated time commitments set proper expectations for survey length.
Newsletter Signup Forms
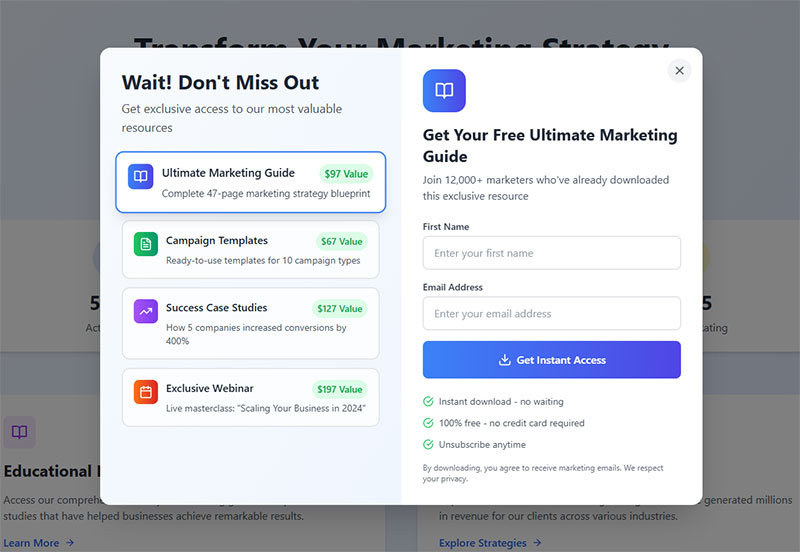
Newsletter subscription forms capture email addresses for marketing campaigns and content distribution. They serve as primary lead generation tools for content marketing strategies.
Conversion Performance Metrics
- Average Conversion Rate: Email collection forms achieve 15% conversion rates
- Placement Impact: Above-the-fold forms capture 57% more page viewing time
- Modal vs Static: Static forms outperform popup modals 45.53% to 25.96%
- Mobile Optimization: Responsive designs increase mobile conversions by 25%
Form Placement & Design Strategy
Strategic placement includes website headers, sidebars, content areas, and exit-intent popups. A/B testing determines optimal positioning for different audience segments.
Incentive offers like exclusive content, discounts, and free resources increase subscription rates. Value propositions clearly communicate benefits of newsletter subscriptions.
Email Marketing Integration
Newsletter forms connect with email service providers including Mailchimp, ConvertKit, and ActiveCampaign. Automated welcome sequences engage new subscribers with relevant content.
Segmentation options allow subscribers to choose content categories and email frequency preferences.
Compliance & Privacy
GDPR compliance requires explicit consent checkboxes and clear privacy policy links. Double opt-in processes confirm subscriber intent and improve email deliverability rates.
Unsubscribe options must appear in all email communications with one-click removal functionality.
Checkout Forms
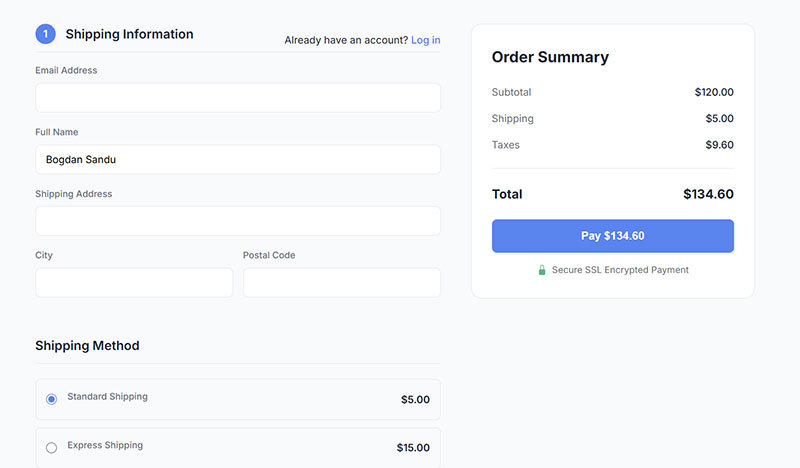
E-commerce checkout forms process transactions and collect payment information. They represent the final conversion step in online purchase funnels.
Transaction Performance Data
- Completion Time: Average checkout takes 3 minutes 21 seconds
- Abandonment Rate: 70% of shopping carts are abandoned before completion
- Mobile Conversion: Mobile checkouts convert 2% versus 3% on desktop
- Field Optimization: Reducing fields from 11 to 4 increases conversions by 120%
Payment Processing & Security
Secure payment gateways process credit cards, digital wallets, and alternative payment methods. SSL encryption protects sensitive financial information during transmission.
PCI compliance ensures payment data handling meets industry security standards. Fraud detection systems monitor transactions for suspicious activity patterns.
User Experience Elements
Guest checkout options eliminate account creation requirements that cause abandonment. Auto-fill capabilities reduce manual data entry for returning customers.
Progress indicators show checkout steps while breadcrumb navigation allows easy section switching. Error handling provides clear guidance for form completion issues.
Advanced Checkout Features
One-click purchasing stores payment information for instant transactions. Multiple payment options accommodate customer preferences including PayPal, Apple Pay, and cryptocurrency.
Shipping calculators show delivery costs and timeframes before purchase completion. Tax calculations update automatically based on shipping addresses.
Job Application Forms
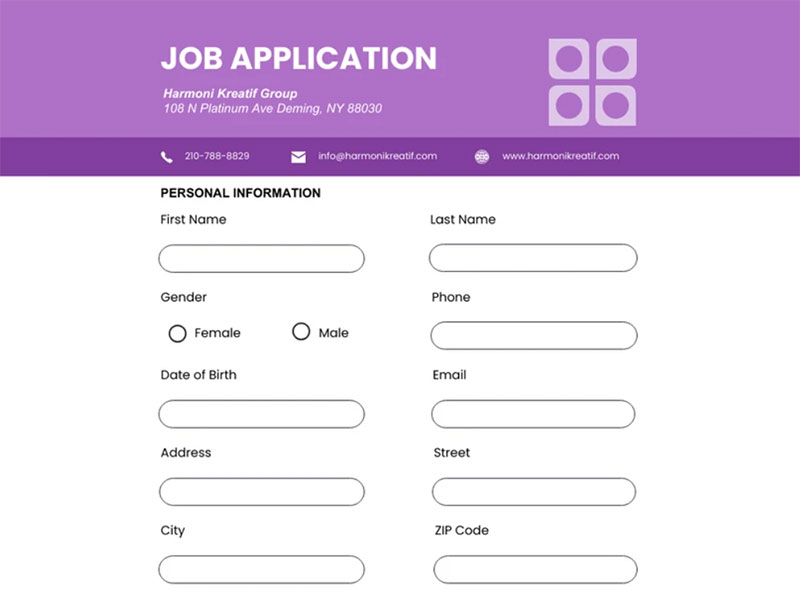
Image source: Venngage
Employment application forms collect candidate information and evaluate job qualifications. They streamline recruitment processes while ensuring legal compliance.
Recruitment Metrics & Performance
- Abandonment Rate: 60% of job seekers abandon application forms before completion
- Completion Time: Complex applications require 15-30 minutes
- Mobile Usage: 70% of job searches occur on mobile devices
- Quality Screening: Longer forms filter unqualified candidates effectively
Application Components & Structure
Job applications collect personal information, work history, education details, and references. Skills assessments and personality tests evaluate candidate fit.
File upload forms accept resumes, cover letters, and portfolio samples. Document format restrictions ensure compatibility with applicant tracking systems.
Legal Compliance & Equal Opportunity
Employment law compliance prohibits discriminatory questions about age, race, religion, and family status. EEOC guidelines govern acceptable inquiry topics.
Background check disclosures and consent forms meet legal requirements for employment screening processes.
Applicant Tracking Integration
Application forms integrate with recruiting software including Workday, BambooHR, and Greenhouse. Automated screening filters candidates based on qualification criteria.
Communication workflows send status updates and interview scheduling notifications to qualified candidates.
Feedback Forms
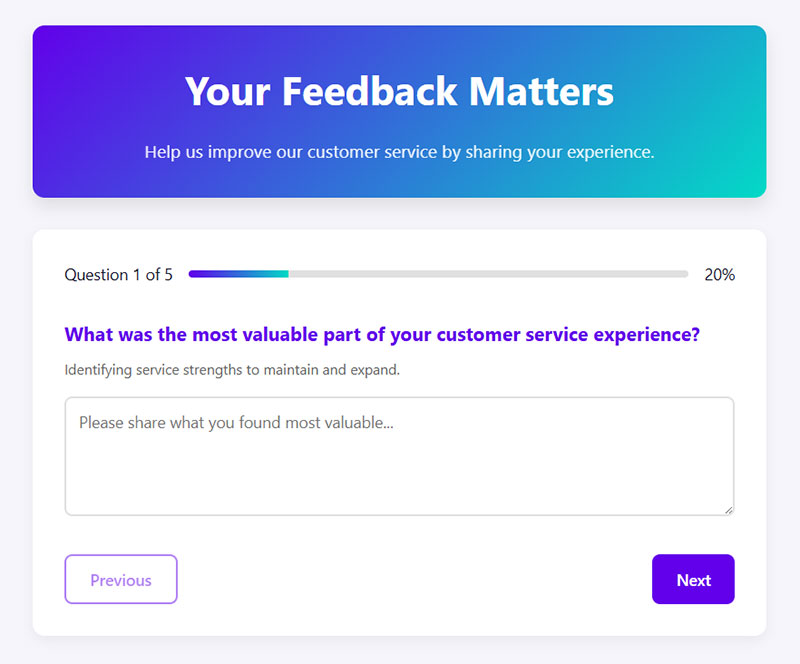
Customer feedback forms collect user opinions, product reviews, and service evaluations. They provide businesses with actionable insights for improvement initiatives.
Feedback Collection Strategies
- Response Timing: Post-purchase surveys achieve highest response rates
- Question Types: Rating scales, multiple choice, and open-ended responses
- Incentive Programs: Discounts and rewards increase participation by 40%
- Follow-up Actions: Response acknowledgments improve customer relationships
Form Design & User Experience
Feedback forms use rating scales for quantitative measurements and text areas for detailed comments. Star ratings provide intuitive evaluation methods.
Conditional logic reveals follow-up questions based on satisfaction ratings. Negative feedback triggers additional support options and resolution workflows.
Data Analysis & Reporting
Feedback platforms generate reports showing satisfaction trends and improvement opportunities. Sentiment analysis categorizes text responses as positive, negative, or neutral.
Integration with customer service systems creates support tickets for negative feedback requiring immediate attention.
Implementation Best Practices
Timing optimization sends feedback requests at moments when customers are most engaged. Multi-channel distribution includes email, SMS, and in-app notifications.
Anonymous feedback options encourage honest responses while identified submissions enable personalized follow-up communications.
Search Forms
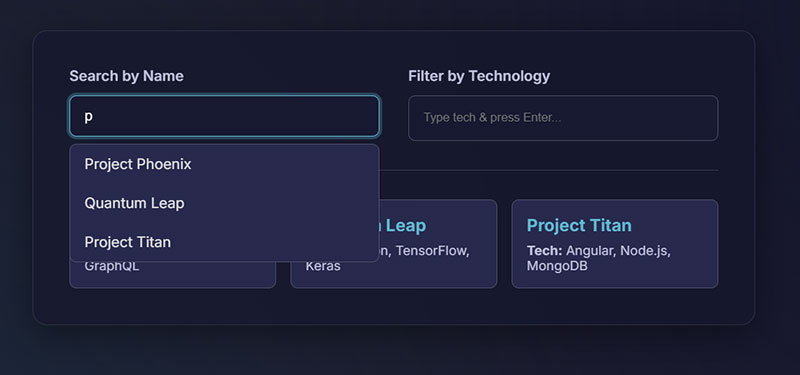
Website search forms help users find specific content, products, and information. They improve user experience and provide valuable insights into user intent.
Search Functionality & Performance
- Usage Patterns: 30% of website visitors use internal search functions
- Query Length: Average search queries contain 2-3 words
- Result Relevance: Poor search results increase bounce rates by 50%
- Mobile Optimization: Touch-friendly search interfaces improve mobile engagement
Search Algorithm & Features
Advanced search forms include filters for categories, price ranges, and product attributes. Auto-complete functionality suggests search terms as users type.
Typo tolerance handles misspelled queries while synonym recognition expands search capabilities. Search history provides personalized suggestions based on previous queries.
User Interface Design
Search boxes use prominent placement in website headers with recognizable magnifying glass icons. Placeholder text provides search examples and guidance.
Advanced search options allow boolean operators and complex query construction for power users.
Analytics & Optimization
Search analytics track popular queries, zero-result searches, and user behavior patterns. Heat mapping shows search interaction patterns and optimization opportunities.
A/B testing evaluates different search interface designs and functionality improvements.
Multi-Step Forms
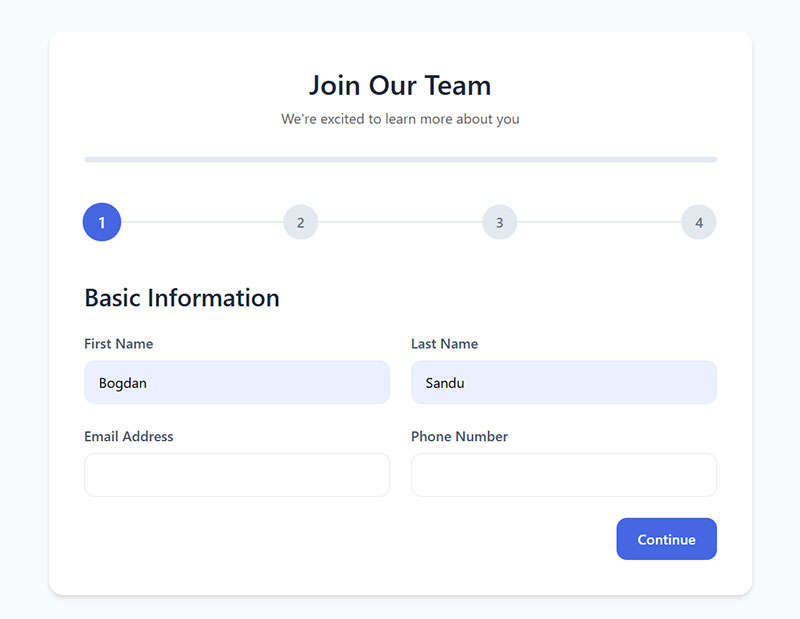
Multi-step forms break complex data collection into manageable sections. They improve user experience while maintaining comprehensive information gathering.
Performance Benefits & Metrics
- Conversion Advantage: Multi-step forms convert 86% higher than single-page alternatives
- Completion Rates: Step-by-step forms achieve 13.85% versus 4.53% for single-page designs
- User Engagement: Progress indicators reduce abandonment by showing completion status
- Mobile Optimization: Simplified steps improve mobile form completion
Design Architecture & Flow
Logical step sequences group related information together. Personal details, preferences, and confirmation steps create natural progression flows.
Progress bars show completion percentage while breadcrumb navigation enables step-by-step movement. Save and resume functionality allows users to complete forms across multiple sessions.
Technical Implementation
Form state management preserves data between steps while validation occurs at each stage. Conditional logic shows relevant steps based on user responses.
Error handling identifies incomplete sections without forcing users to restart entire forms.
Use Case Applications
E-commerce checkouts benefit from separated billing, shipping, and payment steps. Lead generation forms collect basic information before requesting detailed preferences.
Application processes break lengthy requirements into digestible sections that reduce user fatigue.
File Upload Forms
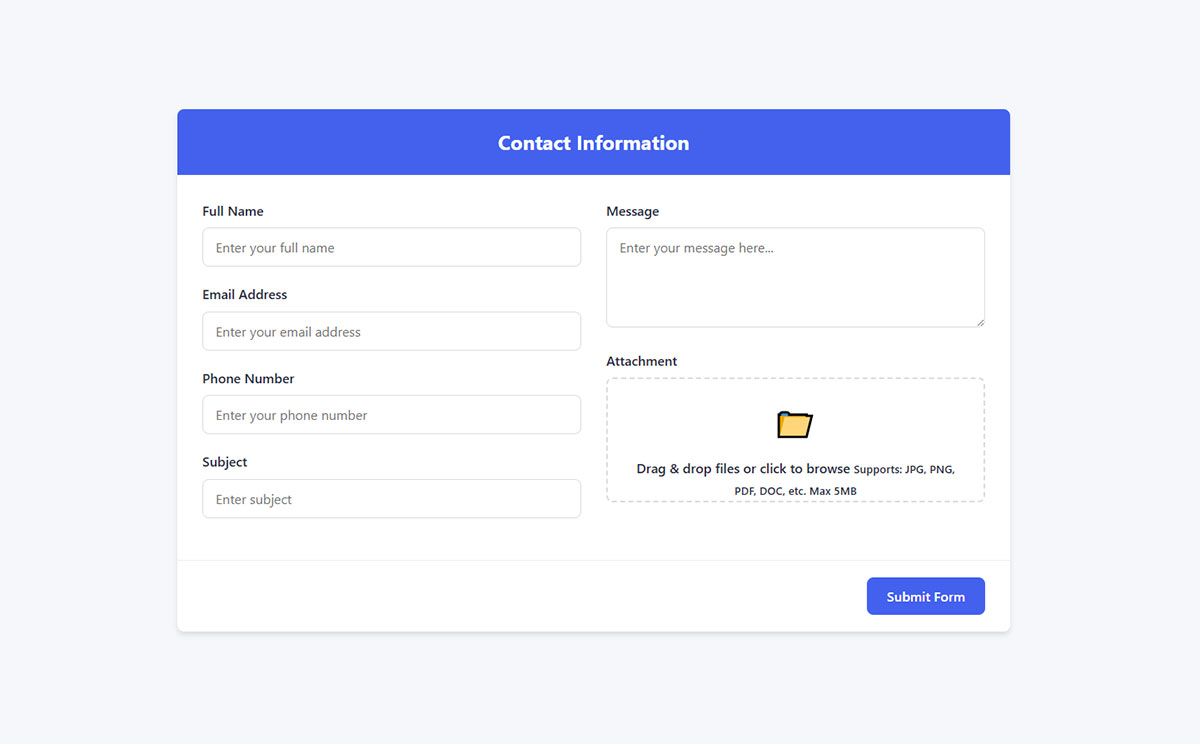
File upload forms enable document submission, image sharing, and content creation. They handle various file types while ensuring security and performance.
Upload Capabilities & Restrictions
- File Types: Documents (PDF, DOC), images (JPG, PNG), videos (MP4, AVI)
- Size Limits: Typical restrictions range from 10MB to 100MB per file
- Multiple Files: Batch upload functionality improves user efficiency
- Progress Indicators: Upload progress bars show completion status
Security Measures & Validation
File type validation prevents malicious uploads while virus scanning protects against security threats. File size restrictions maintain server performance and storage efficiency.
Secure file storage uses encrypted cloud services with access controls and expiration policies.
User Experience Features
Drag-and-drop interfaces simplify file selection while thumbnail previews confirm correct file uploads. File naming conventions help organize uploaded content.
Error handling provides clear feedback for unsupported formats and oversized files.
Integration & Processing
Upload forms connect with cloud storage services including AWS S3, Google Drive, and Dropbox. Automated processing extracts metadata and generates file previews.
Workflow integration triggers approval processes and notification systems for uploaded documents.
Payment Forms
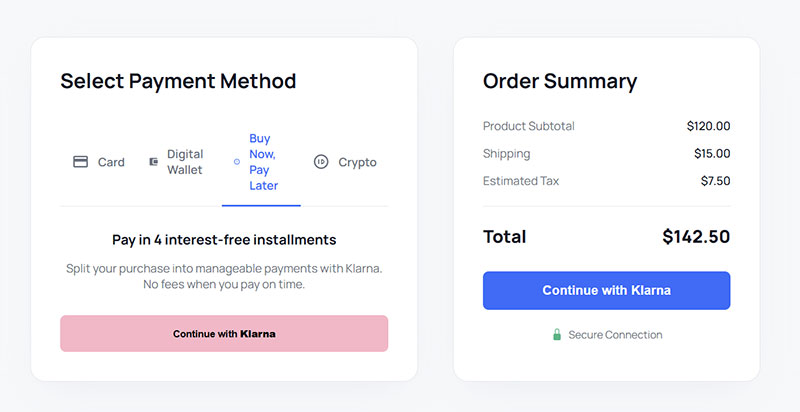
Online payment forms process financial transactions securely while maintaining user trust. They integrate with payment processors and comply with financial regulations.
Payment Processing Standards
- Security Compliance: PCI DSS certification required for payment handling
- Encryption: SSL/TLS encryption protects payment data transmission
- Fraud Detection: Real-time monitoring identifies suspicious transactions
- Payment Methods: Credit cards, digital wallets, bank transfers, cryptocurrency
Form Design & Trust Elements
Payment forms display security badges and SSL certificates to build user confidence. Clear pricing information includes taxes, fees, and total amounts.
Payment method icons show accepted card types while CVV explanations help users locate security codes.
Transaction Management
Payment processing integrates with gateways including Stripe, PayPal, and Square. Automated receipts confirm successful transactions with detailed breakdowns.
Refund processing handles returns and cancellations through integrated merchant systems.
Compliance & Regulation
Financial regulations require transparent pricing and cancellation policies. Data retention policies specify payment information storage timeframes.
International payments comply with regional regulations and currency conversion requirements.
Booking Forms
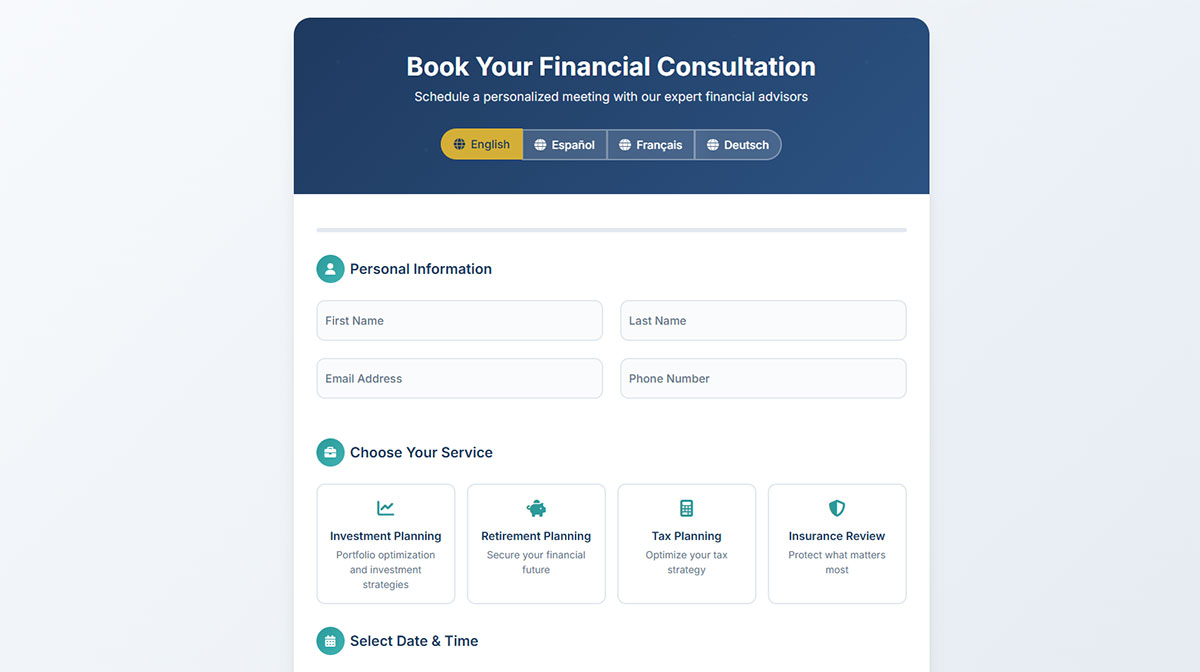
Reservation and appointment booking forms manage scheduling for services, events, and resources. They integrate with calendar systems and automate confirmation processes.
Scheduling Functionality & Features
- Calendar Integration: Real-time availability checking prevents double bookings
- Time Slot Management: Customizable booking windows and duration settings
- Automated Confirmations: Email and SMS notifications confirm reservations
- Cancellation Policies: Flexible rescheduling and refund options
Booking Process & User Experience
Date and time selection uses intuitive calendar interfaces with available slot highlighting. Service selection includes descriptions, pricing, and duration information.
Customer information collection includes contact details and special requirements. Payment integration processes deposits and full payments at booking time.
Business Integration & Management
Booking systems integrate with existing calendar platforms including Google Calendar and Outlook. Staff scheduling coordinates provider availability with customer requests.
Resource management tracks equipment, room, and service provider availability across multiple booking channels.
Industry Applications
Healthcare booking manages patient appointments with provider specializations and insurance requirements. Restaurant reservations handle table availability and party size requirements.
Event booking processes ticket sales with seating selection and group discounts.
Profile Forms
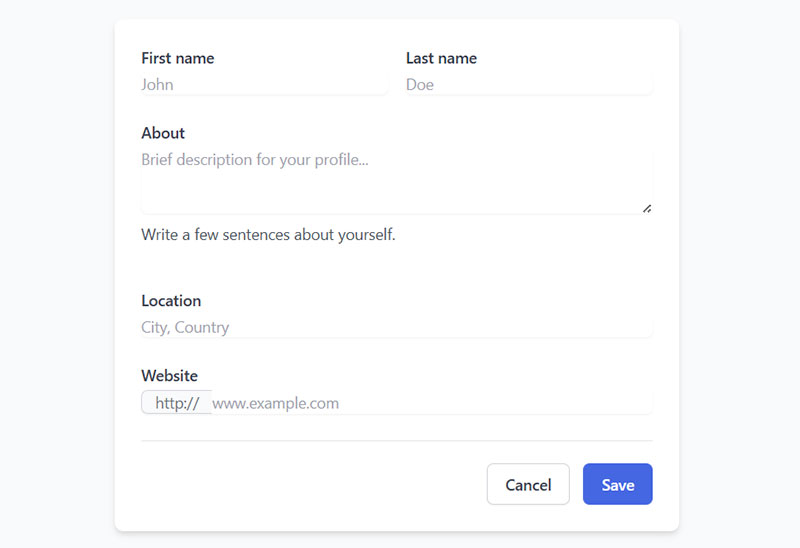
User profile forms collect personal information and preferences for account customization. They enable personalization while respecting privacy preferences.
Profile Data Collection
- Personal Information: Name, contact details, demographics, preferences
- Privacy Controls: Visibility settings and data sharing preferences
- Customization Options: Theme selection, notification preferences, language settings
- Security Settings: Password changes, two-factor authentication setup
User Experience & Interface
Profile editing uses tabbed interfaces organizing information into logical sections. Real-time saving prevents data loss during extended editing sessions.
Image upload functionality enables profile photo and background customization. Privacy explanations help users understand data usage and sharing policies.
Data Management & Security
Profile information integrates with user authentication and personalization systems. Privacy controls allow users to limit data visibility and sharing.
Data export options provide users with complete profile information downloads for portability.
Personalization Features
Preference settings customize content recommendations and user interface elements. Notification controls manage email, SMS, and push notification delivery.
Account linking connects profiles with social media and external service accounts.
Address Forms
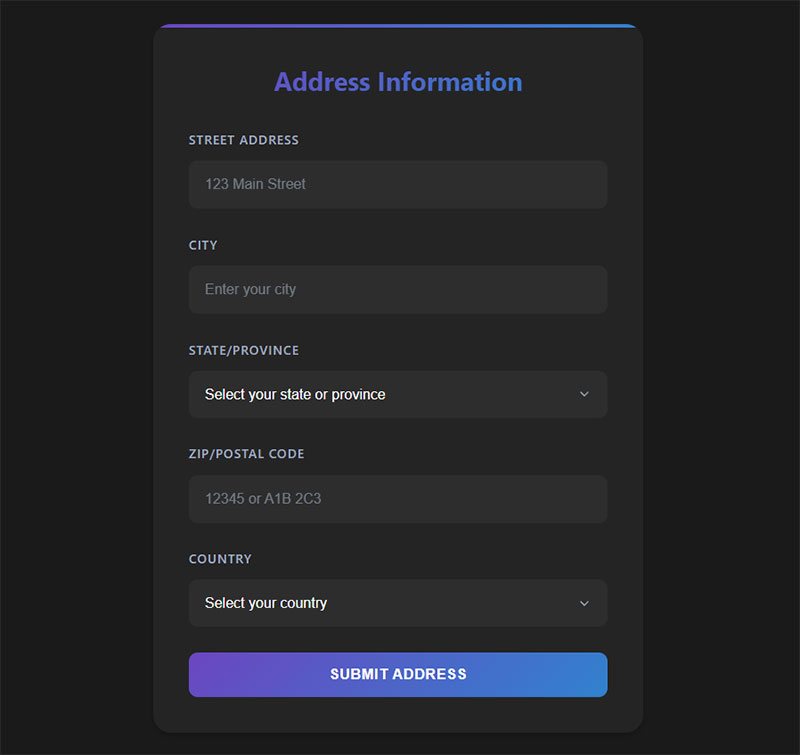
Address collection forms gather location information for shipping, billing, and contact purposes. They ensure accuracy while accommodating international formatting requirements.
Address Validation & Formatting
- International Support: Country-specific address formats and postal codes
- Auto-Complete: Address suggestion as users type
- Validation Services: Real-time verification against postal databases
- Geocoding: Converting addresses to latitude/longitude coordinates
Form Structure & Components
Address forms collect street addresses, cities, states/provinces, postal codes, and countries. Separate billing and shipping address options accommodate different delivery requirements.
Address book functionality saves frequently used addresses for faster form completion. Default address selection streamlines repeat transactions.
Technical Integration & APIs
Address validation services integrate with USPS, Canada Post, and international postal systems. Mapping integration shows address locations for verification.
Shipping calculators use address information to determine delivery costs and timeframes.
User Experience Optimization
Smart formatting automatically adjusts address fields based on selected countries. Error handling provides specific guidance for address formatting requirements.
Mobile optimization includes large input fields and simplified country selection interfaces.
Quiz Forms
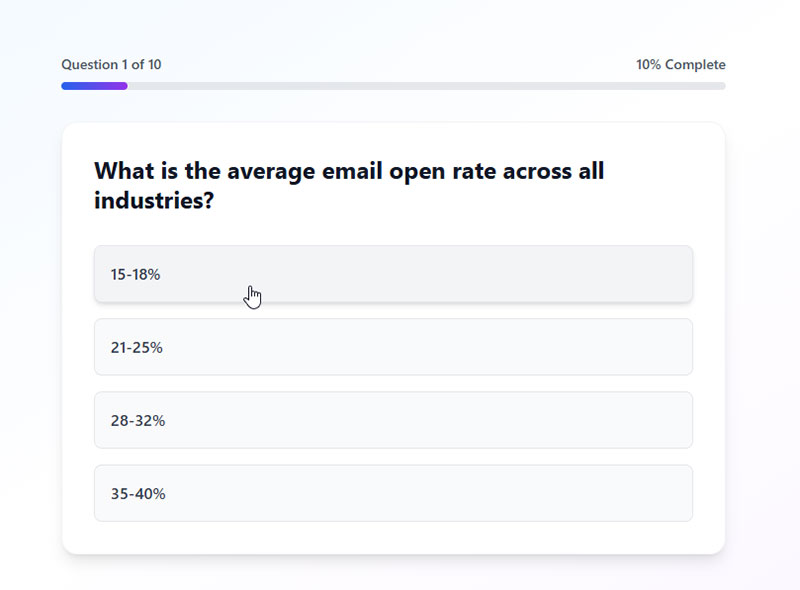
Interactive quiz forms engage users while collecting lead information and providing personalized results. They combine entertainment with data collection for marketing purposes.
Engagement & Performance Metrics
- Conversion Impact: Quiz forms triple conversion rates compared to static forms
- Completion Rates: Interactive elements increase completion by 40%
- Lead Quality: Quiz participants show higher engagement with follow-up marketing
- Social Sharing: Results sharing expands reach through social media
Quiz Design & Structure
Question types include multiple choice, true/false, image selection, and rating scales. Branching logic creates personalized question paths based on previous answers.
Results pages provide detailed analysis with actionable recommendations. Lead capture occurs before results revelation to ensure data collection.
Gamification Elements
Scoring systems track correct answers and performance metrics. Progress indicators show quiz completion status while time limits add urgency.
Achievement badges and completion certificates increase user satisfaction and sharing behavior.
Marketing Integration & Follow-up
Quiz results trigger personalized email sequences with relevant content and product recommendations. Segmentation tags categorize leads based on quiz responses.
Social media integration enables results sharing with custom graphics and messaging.
Support Ticket Forms
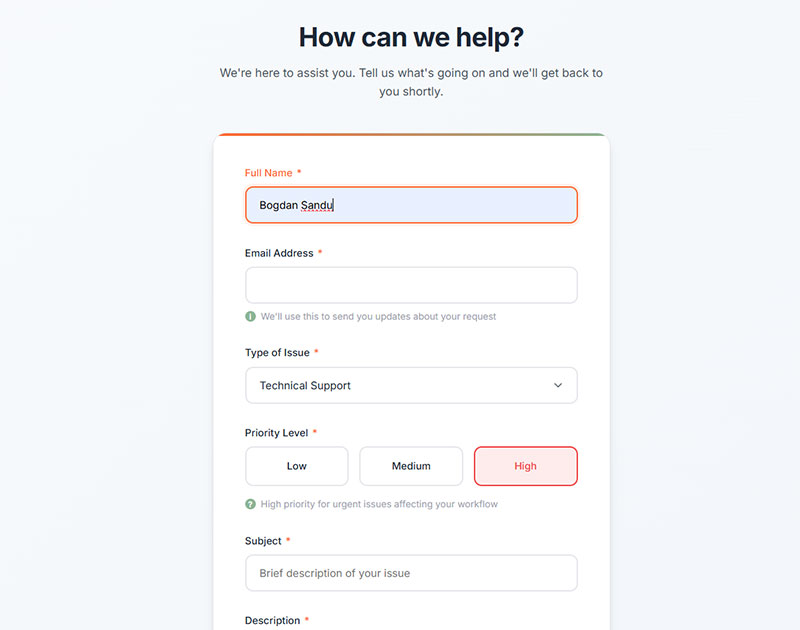
Customer support forms create structured problem reports and service requests. They streamline issue resolution while collecting necessary troubleshooting information.
Ticket Management & Workflow
- Priority Classification: Urgent, high, medium, low priority levels
- Category Selection: Technical, billing, product, general inquiry options
- Agent Assignment: Automatic routing based on expertise and availability
- Status Tracking: Open, in progress, pending, resolved ticket states
Problem Description & Details
Support forms collect detailed problem descriptions with steps to reproduce issues. Screenshot and file attachment capabilities provide visual context.
System information collection includes browser types, operating systems, and product versions for technical troubleshooting.
Integration & Automation
Ticket systems integrate with knowledge bases to suggest self-service solutions. Automated responses acknowledge ticket receipt and provide estimated response times.
Escalation workflows route complex issues to specialized support teams based on predefined criteria.
Performance Tracking & Analytics
Response time tracking monitors support team performance and customer satisfaction. Ticket resolution reports identify common issues and improvement opportunities.
Customer feedback collection evaluates support quality and identifies training needs.
Event Registration Forms
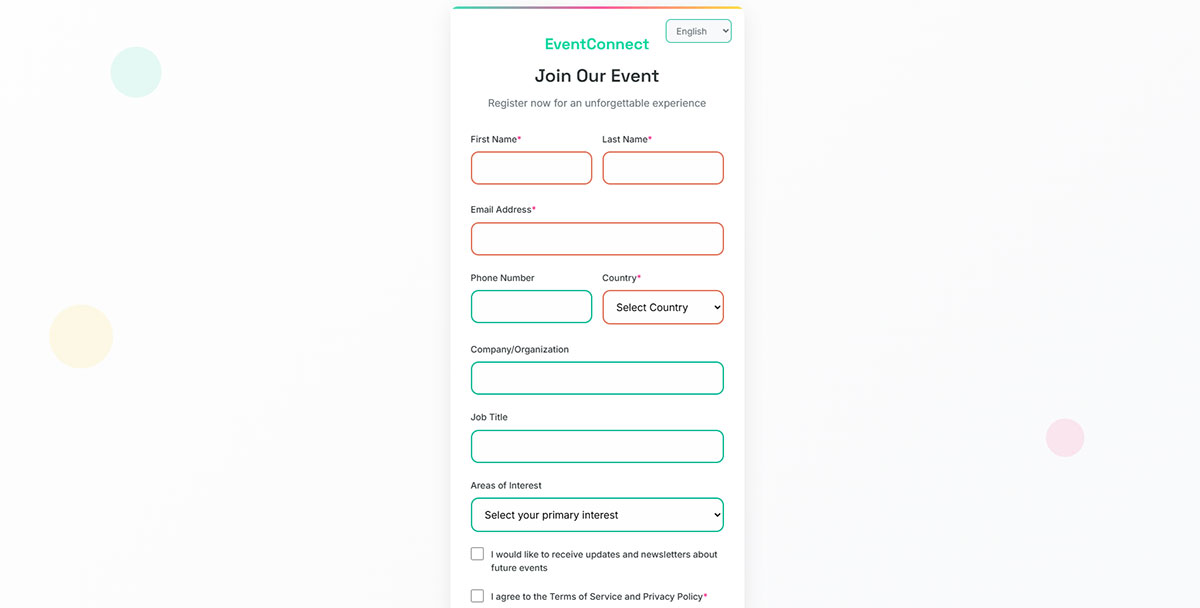
Event signup forms manage attendee registration for conferences, workshops, and social gatherings. They handle capacity limits, payment processing, and communication workflows.
Registration Management Features
- Capacity Controls: Maximum attendee limits with waitlist functionality
- Pricing Tiers: Early bird, regular, group, and student pricing options
- Session Selection: Workshop choices and agenda customization
- Dietary Requirements: Meal preferences and allergy information
Payment & Confirmation Processing
Integrated payment processing handles registration fees with multiple payment method support. Group discounts apply automatically based on registration quantities.
Confirmation emails include event details, schedules, and venue information. Calendar integration adds events to attendee personal calendars.
Attendee Communication & Updates
Automated email sequences provide pre-event information and reminders. Event updates and schedule changes reach all registered attendees instantly.
Badge printing integration generates name tags and identification materials from registration data.
Event Analytics & Reporting
Registration tracking monitors signup patterns and capacity utilization. Demographic reporting provides insights into attendee composition and marketing effectiveness.
Revenue tracking calculates total registration income with payment method breakdowns.
Subscription Forms
Recurring service signup forms establish ongoing billing relationships and service access. They manage subscription tiers, billing cycles, and cancellation processes.
Subscription Management Features
- Pricing Plans: Monthly, annual, and custom billing cycles
- Trial Periods: Free trial access with automatic conversion
- Plan Upgrades: Seamless tier changes with prorated billing
- Cancellation Policies: Self-service cancellation and retention offers
Billing Integration & Processing
Subscription forms integrate with recurring billing systems including Stripe Billing and Chargebee. Automated invoice generation and payment processing reduce manual administration.
Failed payment handling includes retry logic and dunning management for expired cards.
Customer Onboarding & Activation
Welcome sequences guide new subscribers through service setup and feature discovery. Progress tracking monitors subscription activation and usage patterns.
Support integration provides easy access to help resources and customer service contacts.
Retention & Growth Strategies
Subscription forms include referral programs and upgrade incentives to drive growth. Cancellation surveys collect feedback for service improvement.
Win-back campaigns target cancelled subscribers with special offers and feature updates.
Product Order Forms
E-commerce order forms facilitate product selection, customization, and purchase completion. They integrate inventory management with payment processing for seamless transactions.
Product Configuration & Selection
- Variant Options: Size, color, style, and customization choices
- Quantity Selection: Bulk pricing and volume discounts
- Product Bundles: Related item suggestions and package deals
- Inventory Tracking: Real-time stock level displays
Pricing & Calculation
Dynamic pricing updates automatically based on selected options and quantities. Shipping calculations provide accurate delivery costs based on location and product dimensions.
Tax calculations handle regional requirements and exemption certificates. Discount codes apply promotional pricing and loyalty program benefits.
Order Processing & Fulfillment
Order forms integrate with inventory management and fulfillment systems. Automated order confirmation includes tracking information and delivery estimates.
Customer service integration enables order modifications and cancellation requests.
Performance Optimization & Analytics
Conversion tracking identifies optimization opportunities in the ordering process. A/B testing evaluates different form layouts and pricing presentation methods.
Cart abandonment tracking triggers recovery emails with personalized incentives and reminders.
What is Form Design
Form design is the process of structuring input fields, labels, buttons, and visual elements so users can submit information through a digital interface. It covers everything from field order to error handling to the size of a submit button on a 375px screen.
Every website form you fill out, whether it’s a three-field newsletter signup or a 20-field insurance quote, was designed with some level of intention. Or at least it should have been.
The scope goes beyond just “making it look nice.” Form design directly touches usability, accessibility, conversion rates, and data quality. A poorly structured checkout form on Shopify loses revenue. A confusing registration form on a SaaS product kills onboarding.
The core components include input field types, label placement, visual hierarchy, validation logic, error messages, and CTA button design. These elements work together, not in isolation.
How Does Form Design Affect User Experience
Bad form design creates friction, and friction kills completion rates. Baymard Institute found that 18% of users have abandoned a checkout in the last quarter solely due to a “too long or complicated checkout process.”
Every decision matters: where you place labels, how you handle form validation, what happens when someone enters an invalid email. Luke Wroblewski’s research on top-aligned labels versus left-aligned labels showed a measurable difference in completion times. Top-aligned labels won.
Form UX design also covers less obvious things like tab order between fields, autofill compatibility, and whether your date picker actually works on mobile Safari. These details compound.
What Are the Main Types of Web Forms
There are several distinct types of forms used across websites and apps, each built for a specific purpose:
- Contact forms collect name, email, and a message for general inquiries
- Registration forms handle account creation for SaaS products, communities, or services
- Checkout forms process payment, shipping, and billing during e-commerce transactions
- Multi-step forms break long processes into smaller screens, common in insurance, finance, and onboarding
- Survey forms gather feedback or research data through multiple question types
- Login forms authenticate returning users with email/password or social sign-in
- Subscription forms capture email addresses for newsletters, updates, or content access
- Intake forms collect detailed client information for service-based businesses
Each type has its own set of best practices. A contact form with 12 fields is doing it wrong. An intake form with only 3 fields probably isn’t collecting enough.
What Makes a Good Form Design
A good form design reduces cognitive load, guides the user through each step, and collects the right data without unnecessary friction. That’s it. Everything else is a detail supporting one of those three goals.
The measurable qualities include high completion rates, low abandonment, minimal validation errors, and fast time-to-submit. If your form hits those benchmarks, the design is working.
How Many Input Fields Should a Form Have
Fewer fields almost always means higher conversion. HubSpot tested this and found that reducing form fields from 4 to 3 increased conversions by nearly 50%. The right number depends on context, but the principle holds: every additional field costs you completions.
For lead generation forms, 3 to 5 fields is the standard range. For checkout, you can’t avoid asking for shipping and payment details, but you can remove the “Company Name” field nobody needs. Know which form fields actually matter for your goal and cut everything else.
What is Inline Validation in Forms
Inline validation checks user input in real time, right next to the field, instead of waiting until the user hits submit. It shows a green checkmark when an email format is correct or a red form error message when a password is too short.
This pattern reduces form errors by roughly 22%, according to research from the Nielsen Norman Group. It works best on email fields, password strength indicators, and phone number formatting. Don’t validate fields that are still being typed in. Wait until the user moves to the next field.
What Role Does Visual Hierarchy Play in Form Layout
Visual hierarchy tells users where to look first, what to fill in next, and where to click when they’re done. Without it, even a five-field form feels overwhelming.
The key layout decisions:
- Label placement: top-aligned labels perform best for speed; floating labels save space but can cause accessibility issues
- Field grouping: related inputs (like first name and last name) should sit together visually
- Whitespace: generous spacing between field groups reduces perceived complexity
- Progress indicators: for multi-step forms, showing “Step 2 of 4” keeps users oriented
- CTA button: the submit button should be the most visually prominent element on the form
Single-column form layouts outperform multi-column layouts in nearly every test. Google’s Material Design guidelines recommend single-column for this exact reason.
FAQ on Form Design
What is form design?
Form design is the process of structuring input fields, labels, buttons, and validation logic within a digital interface. It covers layout, visual hierarchy, error handling, and field types to help users submit information quickly and accurately across websites and mobile apps.
What makes a form design effective?
An effective form minimizes cognitive load, uses clear labels, applies inline validation, and limits field count to what’s necessary. High completion rates and low abandonment are the measurable signs. Single-column layouts and top-aligned labels consistently outperform other patterns.
How many fields should a form have?
It depends on the form’s purpose. Landing page forms perform best with 3 to 5 fields. Checkout forms need more but should cut anything non-essential. Every extra field lowers your conversion rate.
What are the best form design examples for registration pages?
Single-column layouts with 3 to 4 fields, social login options (Google, Apple, Facebook), and progressive disclosure patterns work best. Airbnb, Notion, and Slack all use minimal registration form designs that prioritize speed over data collection upfront.
How does form design affect conversion rates?
Directly. Baymard Institute research shows better checkout form design alone can increase conversions by 35%. Field reduction, clear error messages, autofill support, and mobile form optimization are the biggest factors that move the numbers.
What is the difference between single-step and multi-step forms?
Single-step forms show all fields on one screen. Multi-step forms split them across multiple screens with progress indicators. Short forms work better as single-step. Complex processes like insurance applications or onboarding flows benefit from multi-step layouts.
What are common form design mistakes?
Too many required fields, missing error messages, no mobile optimization, unclear CTA button text, and forcing account creation before checkout. Poor form accessibility is another common issue, especially missing label associations and low contrast ratios.
How do you design forms for mobile users?
Use single-column layouts, thumb-friendly tap targets (minimum 44x44px), native input types like tel and email, and sticky submit buttons. Reduce typing through dropdowns and toggles. Avoid multi-column grids, which break on smaller screens.
What role does validation play in form design?
Validation prevents bad data and reduces user frustration. Inline validation (checking fields in real time) reduces errors by roughly 22% compared to post-submit validation. It works best on email fields, password strength, and formatted inputs like phone numbers.
Should forms use placeholder text instead of labels?
No. Placeholders disappear once users start typing, which creates confusion. Always use visible labels. Placeholders work as supplementary hints (like “e.g., [email protected]”) but should never replace labels entirely. The Nielsen Norman Group and WCAG guidelines both advise against it.
Conclusion
Good form design examples share the same DNA: clear labels, minimal fields, logical flow, and validation that helps instead of punishes. Whether you’re building a checkout page in Shopify or a signup screen in Figma, those principles don’t change.
Pick the pattern that fits your use case. A three-field contact form template for a portfolio site. A progressive disclosure flow for fintech onboarding. A guest checkout for your e-commerce store.
Then test it. Watch session recordings. Check your completion rates and conversion rate benchmarks against industry averages.
The best form isn’t the one that looks the prettiest in a Dribbble shot. It’s the one people actually finish filling out. Start with the examples that match your goals, optimize your forms based on real user behavior, and cut everything that gets in the way.