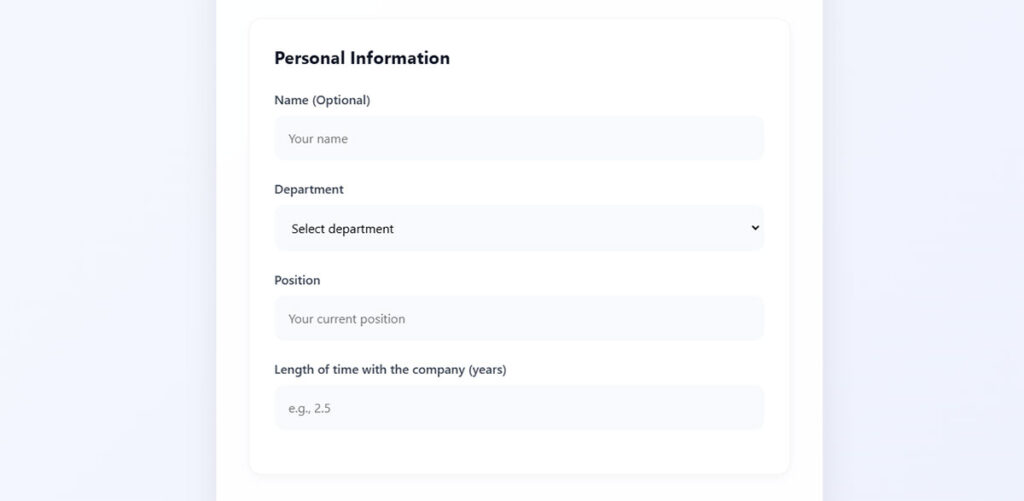
A poorly designed form can kill your conversion rates instantly. Landing page form best practices aren’t just nice-to-have guidelines—they represent the difference between turning visitors into leads or watching them abandon your…
Table of Contents
Poor feedback collection kills business growth faster than any competitor ever could.
Companies lose millions in potential revenue because their feedback forms drive users away instead of drawing them in. Customer satisfaction drops when businesses fail to gather meaningful insights through proper data collection methods.
Best practices for creating feedback forms transform how organizations understand their audience and improve their offerings. Smart form design principles boost response rates while user experience design ensures completion rather than abandonment.
This guide reveals proven strategies for crafting feedback forms that actually work. You’ll discover how to structure questions, optimize form layout, implement form validation, and create interactive elements that encourage participation.
Learn to build forms that deliver actionable insights, increase user engagement, and drive real business results. From mobile responsiveness to accessibility standards, every element matters when collecting valuable customer data.
Types of Feedback Forms
Customer Feedback Forms
See the Pen
Modern Customer Feedback Form by Bogdan Sandu (@bogdansandu)
on CodePen.
CSAT (Customer Satisfaction Score) measures how satisfied customers are with a product or service.
This involves short surveys that ask straightforward questions about the customer’s overall satisfaction. It’s simple but can quickly tell you where you stand with your customers.
NPS (Net Promoter Score) asks customers how likely they are to recommend your product or service to others on a scale of 0 to 10.
This type of feedback form helps in understanding customer loyalty. Customers are categorized as promoters, passives, or detractors based on their scores, which can guide more targeted follow-ups and improvements.
CES (Customer Effort Score) evaluates how much effort a customer has to put in to get their issue resolved, or to use a product/service.
It’s particularly useful for pinpointing friction points in the customer experience. Lower effort scores are usually an indication of a smoother and more satisfactory customer experience.
Employee Feedback Forms
See the Pen
Modern Employee Feedback Form Design by Bogdan Sandu (@bogdansandu)
on CodePen.
Assessing morale, productivity, and support needs gives insights into how employees feel about their work environment, tasks, and the support they receive.
These forms can include multiple-choice questions and open-ended questions to gather both quantitative and qualitative data.
Understanding these aspects allows for better management interventions to boost morale and productivity.
Gathering insights on work environment and resources can reveal how the working conditions and available resources either support or hinder employees.
Questions may range from the effectiveness of current tools to the physical workspace’s suitability. Such feedback forms can guide resource allocation and workplace improvements.
Specialized Feedback Forms
Real Estate Feedback forms are used after a sale, a lease agreement, or by tenants.
These forms can help real estate agents and property managers understand pain points or areas that need improvement.
Feedback might include observations on property conditions, service quality, and overall satisfaction with the transactions.
Product-Market Fit Surveys are designed to understand whether a product meets market needs.
Questions often probe how disappointed customers would be if they could no longer use the product, what features they find most valuable, and where improvements are needed.
This data informs product development and marketing strategies.
Crafting Effective Feedback Forms
Establishing Clear Objectives
Determining what you want to learn is crucial. Whether it’s product improvement or service quality, being clear on your objectives directs the entire survey process.
Establish your goals first to align every question with the focus you need, ensuring your feedback form remains targeted and effective.
Product Improvement involves questions related to features, usability, and satisfaction. What are the user pain points? Which features are indispensable?
Service Quality assessments revolve around customer interactions. Are customers satisfied with the service? Where can improvements be made?
Choosing the Right Question Types
Multiple Choice Questions
Ideal for structured, easy-to-analyze data. These questions limit responses, making them straightforward to quantify.
Great for when you need consistency and quick insights.
Open-Ended Questions
These offer deep insights by allowing respondents to share their thoughts in their own words.
While they are more challenging to analyze, the richness of data you get can provide valuable context and user stories. Perfect for exploratory phases or gaining detailed feedback.
Rating Scales (e.g., Likert Scale)
Useful for assessing customer satisfaction or ease of use. Scales provide a range from “strongly disagree” to “strongly agree”, offering a nuanced view of user opinions.
They’re handy for capturing the intensity of feelings on specific aspects.
Yes/No Questions
These gather binary data quickly and efficiently. Best for clear-cut responses, they help screen for eligibility or initial preferences without overwhelming the respondent.
Structuring Your Form for Clarity and Relevance
Ordering questions logically is key for maintaining flow. Start with broader questions and narrow down to specifics.
This natural progression keeps respondents engaged and reduces drop-off rates.
Using conditional logic enhances relevance. By dynamically showing or hiding questions based on previous answers, you create a tailor-made experience for each respondent.
This reduces the number of irrelevant questions and improves the quality of your data.
For example, using tools like Google Forms or Typeform, you can set up conditions that streamline the user journey, ensuring each question feels pertinent and necessary.
Writing and Designing Feedback Form Questions
Best Practices for Question Clarity
Use straightforward language. No technical jargon. Keep it simple. When you throw in complex terms, you lose your audience.
Bias? Ditch it. Ask neutral questions. You want genuine answers, not guided ones. “How satisfied are you with our service?” works far better than “Why do you love our service?”
Focus on one point per question. Multiple ideas confuse people. You want clarity, not chaos. “Rate your experience with our customer service” beats “Rate your experience with our customer service and product quality.”
Balancing Open and Closed-Ended Questions
Open-ended questions serve a purpose. They provide detailed insights. Let customers speak their minds. This reveals stories and thoughts you didn’t anticipate. It’s raw data, yes, but invaluable.
Closed-ended questions? Efficient. Quick to analyze. A godsend when you’re looking for trends or consensus. Multiple-choice, yes/no, and rating scales—they get you structured data fast.
So balance is key. Mix them up for a healthy data set.
Importance of Survey Length and Completion Time
People have short attention spans. Don’t make the form a marathon. Short forms get more responses. Five minutes is a good target. Push it too long, and you’ll lose them.
Survey length isn’t just about keeping it short. It’s about avoiding fatigue. Each extra question risks another drop-off. Trim the fat. Every question should serve a purpose. UnitOfWork.
Designing for Engagement and Ease of Use
Designing an Intuitive, User-Friendly Layout
When it comes to user-friendly layouts, grouping similar questions together makes a huge difference. Coherence is key.
Don’t scatter your questions randomly—it confuses people. Group by topic. Customer satisfaction questions in one block, product usability in another.
Adding a progress bar? Essential. It helps respondents gauge their progress, reducing the feeling of being overwhelmed.
They know how much is left; it encourages them to finish. Websites like Google Forms and Typeform have these built-in.
Utilizing Branding for Recognition and Trust
Logos, colors, and fonts. Use them. Consistent branding builds trust. When respondents see familiar brand elements, they’re more likely to engage.
Put your logo at the top, use your brand colors, and stick to your company’s fonts. Recognition is immediate.
A conversational tone makes forms more personal. Nobody likes filling out a sterile form. Imagine talking to a friend.
Use phrases like “We’d love your input!” or “How’s our product working for you?”
Multi-Channel Distribution for Maximum Reach
Using email, social media, and website links—this is how you reach people.
Email your existing customers, share the survey on your social media channels, and embed the form on your website. SurveyMonkey and Qualtrics excel in distribution.
Timing and scheduling surveys is strategic. When is your audience most active? For emails, midweek works best. Avoid weekends; engagement drops then. Analyze your audience behavior and time accordingly. Use analytics tools to inform your timing.
Advanced Techniques for Interactive and Engaging Feedback Forms
Applying Conditional Logic
Conditional logic transforms your feedback forms. By showing or hiding questions based on responses, you make each form relevant to the respondent.
This ensures you’re not wasting anyone’s time with irrelevant questions. Tools like Google Forms and Typeform excel at this.
You ask, “Are you satisfied with our service?” A ‘No’ triggers a follow-up question about the issue. A ‘Yes’ skips to the next section.
Enhancing relevance is the goal here. This logical flow keeps the user engaged, avoids fatigue, and makes them feel the form is tailored just for them. Better data. Engaged respondents. Win-win.
Including Visuals and Interactive Elements
Throw in some images or videos. They’re not just eye candy. Use them to clarify questions or provide context. Have a video tutorial? Embed it beside a question asking for feedback on it.
Interactive question formats like sliders ramp up engagement. Instead of another boring checkbox, a slider lets the user feel their response. “On a scale of 1 to 10, how easy was it to use our service?” A slider makes this fun.
Visuals and interactivity make the form feel dynamic. It’s like comparing a lively conversation to a dull monologue. More engagement equals better responses.
Offering Instant Feedback and Acknowledgment
Real-time responses work wonders. Right after they complete a form, thank them. Simple but effective. Use a thank-you page or a follow-up message. SurveyMonkey and Qualtrics have these features.
Thanking respondents reinforces engagement. It lets them know their input is valued. A quick acknowledgment – “Thanks for your feedback!” – can make a difference. You can even tell them how their feedback will be used. This closes the loop and gives a sense of contribution.
Optimizing Feedback Forms for Quality Responses
Encouraging Honest Feedback with Optional Anonymity
Anonymous responses—they’re gold. Offer the option to stay anonymous and watch candid feedback roll in. People open up when they know their identity isn’t in the spotlight.
Privacy expectations are huge. Lay it out clearly: how the data will be used, how it’ll be stored. Transparency builds trust. Assurance from the get-go means more genuine answers.
Offering Incentives to Increase Completion Rates
Incentives work. They motivate action. Think gift cards, discounts, or even entries into a prize draw. Simple but effective to boost your completion rates.
Communicate the benefit of feedback. “Your input helps improve our product.” It’s not just about the reward. It’s about making respondents feel their voice matters.
Testing Feedback Forms Internally
Internal testing is a must. Run the form through its paces with your team. It’s about flow and clarity. Does each question lead naturally to the next? Any confusing parts?
Feedback from colleagues helps. They’ll spot what you might miss. Iron out those kinks internally, and your final form will be solid.
Analyzing and Using Feedback Form Data
Structuring Collected Data for Analysis
Collected data can be a mess or a goldmine. Start by categorizing responses—quantitative and qualitative. Tools like SurveyMonkey and Qualtrics make this easier.
Quantitative data? Think rating scales, yes/no answers, and multiple choice. Numbers. Stats.
Qualitative data? That’s open-ended responses. It’s customer stories and detailed insights.
Organize the qualitative stuff for thematic analysis. Look for patterns and recurring themes. Group similar responses together. Makes it easier to spot trends and common issues.
Interpreting Results to Drive Improvement
Got your data structured? Time to dive in. First, identify key areas for product or service improvements. What are the critical pain points? What do customers love?
Feedback can also inform training. Are there consistent complaints about service quality? That’s a flag. Use the insights to shape your customer service training initiatives.
Reporting Findings to Stakeholders
See the Pen
Employee Feedback Chart Visualization by Bogdan Sandu (@bogdansandu)
on CodePen.
Data’s useless if it sits in a silo. Get those key insights to stakeholders.
Present insights in a concise, actionable format. That means bullet points, not essays. Graphs and charts help too. Visuals make data digestible.
Sharing findings across teams facilitates improvements. Marketing needs to know what’s resonating. Product development needs to know what’s not.
Timely, relevant feedback fuels informed decisions. It’s all about using data to drive action.
FAQ on Best Practices For Creating Feedback Forms
What’s the ideal length for a feedback form?
Keep forms between 5-7 questions maximum. Conversion optimization studies show response rates drop significantly after this point. Focus on essential questions that provide actionable customer insights. Short forms reduce form abandonment and improve completion rates.
How can I improve my feedback form’s response rate?
Use progress indicators, clear call-to-action buttons, and mobile responsiveness. Implement conditional logic to show relevant questions only. Form testing reveals which design principles work best for your audience and user engagement.
Should I use required fields in feedback forms?
Minimize required fields to essential information only. Optional fields encourage voluntary participation while form validation ensures data quality. Balance between gathering necessary data and maintaining positive user experience design.
What question types work best for feedback collection?
Mix rating scales, multiple choice, and open-ended questions. Radio buttons work for single selections, checkboxes for multiple options. Text areas capture detailed responses. Variety keeps users engaged throughout the submission process.
How do I make feedback forms mobile-friendly?
Prioritize mobile responsiveness with touch-friendly input fields, larger buttons, and vertical layouts. Test forms on various devices using Google Analytics data. Mobile forms should load quickly and display properly across all screen sizes.
What’s the best way to handle form errors?
Implement real-time form validation with clear form error message examples. Highlight problematic fields immediately. Error handling should guide users toward successful completion without frustration or confusion.
How can I ensure my feedback forms are accessible?
Follow WCAG guidelines for accessibility standards. Use proper labels, keyboard navigation, and screen reader compatibility. High contrast colors and clear typography improve form accessibility for all users, including those with disabilities.
Should I include a progress bar in multi-step forms?
Yes, progress indicators reduce abandonment in multi-step forms. Users need to understand their completion status. Visual progress bars set expectations and encourage form completion through each step.
What’s the best placement for feedback forms on websites?
Strategic placement depends on your goals. Exit intent popup forms capture leaving visitors. Landing page forms work for targeted campaigns. Contact us page forms provide dedicated feedback channels. Test different locations for optimal user behavior tracking.
How do I write effective confirmation messages?
Create clear form submission confirmation message content that acknowledges receipt and sets expectations. Include next steps, timeline for response, and contact information. Good confirmation messages build trust and complete the feedback loops.
Conclusion
Implementing best practices for creating feedback forms transforms how organizations collect and analyze customer data. Effective survey creation drives meaningful user input while maintaining high usability testing standards.
Form optimization requires attention to multiple elements:
- Question types that encourage honest responses
- Database integration for seamless response management
- Thank you pages that complete the user journey mapping
- Email notifications for immediate response tracking
Lead generation success depends on balancing comprehensive data collection methods with streamlined form structure. CRM systems benefit from well-designed questionnaire development that captures qualified prospects without overwhelming users.
Form analytics reveal which elements boost conversion optimization and reduce form performance issues. A/B testing different dropdown menus, field types, and submission process variations helps identify winning combinations.
Smart feedback analysis turns collected data into actionable business insights. Companies that master these techniques see improved customer satisfaction scores and stronger feedback loops that drive continuous improvement.
If you liked this article about best practices for creating feedback forms, you should check out this article about what are WordPress forms.
There are also similar articles discussing types of forms, WordPress form security, how to create forms in WordPress without plugins, and how to create registration forms in WordPress without a plugin.
And let’s not forget about articles on form validation best practices, form accessibility best practices, how to create GDPR compliant forms, and sign up form best practices.