Most forms lose people before they finish. Long field lists, confusing layouts, zero feedback when something goes wrong. That’s the reality for static forms on most websites. Interactive forms fix…
Table of Contents
Every failed form submission drives potential customers away from your website. Poor validation messages frustrate users, increase abandonment rates, and cost businesses real money.
Form validation best practices separate professional web applications from amateur attempts. Modern users expect instant feedback when they make mistakes during data entry. They want clear guidance, not cryptic error codes.
Client-side validation provides immediate user feedback while server-side validation ensures data security. Real-time validation catches mistakes early, and proper error handling feels supportive rather than critical.
This guide covers validation timing, error message design, input sanitization, and mobile optimization strategies. You’ll learn when to validate, how to display feedback, and which JavaScript frameworks work best for different scenarios.
By the end, you’ll know how to build forms that convert users instead of confusing them. Your validation will guide naturally while protecting against security vulnerabilities and improving accessibility compliance.
Form Validation Best Practices
Use Client-Side Validation for Immediate Feedback
See the Pen
Modern Sign Up Form With Inline Validation by Bogdan Sandu (@bogdansandu)
on CodePen.
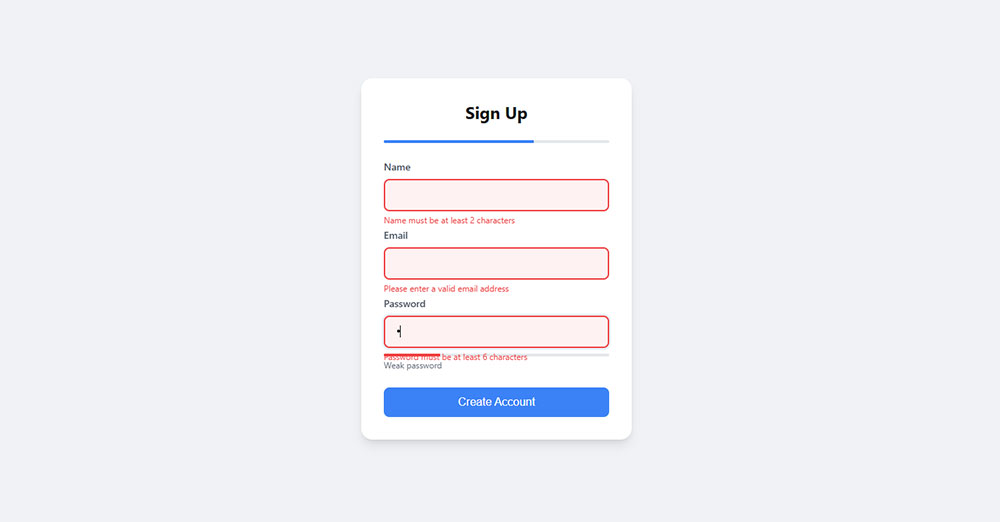
Client-side validation provides immediate feedback to users as they interact with form fields. This validation technique executes in the user’s browser before form submission, catching errors early in the data entry process. The primary function involves checking user input against predefined rules and displaying feedback messages without server communication.
Technical Specifications
Essential attributes for mobile client-side validation implementation:
- Input Type: JavaScript event handlers or HTML5 constraint validation
- Touch Target Size: Validation messages require 44px × 44px minimum tap areas for dismissal
- Viewport Behavior: Error messages must not trigger unwanted zoom or viewport shifts
- Validation Method: Real-time validation on blur events, avoiding premature validation during typing
User Experience Impact
Client-side validation reduces form completion time by allowing users to fix errors immediately without waiting for server responses. Measurable improvements include:
- Completion rate improvements of up to 25% for optimized forms
- Error reduction metrics show 22% fewer completion errors
- Task completion time decreases significantly when users receive instant feedback
- Accessibility compliance level meets WCAG 2.1 AA standards with proper ARIA labels
Mobile-Specific Considerations
Device and context factors affecting client-side validation:
- Screen Size Adaptation: Error messages position below fields on mobile, avoiding viewport obstruction
- Touch Interaction: Validation feedback appears after touch events complete, preventing typing interruption
- Keyboard Optimization: Virtual keyboard remains stable during validation feedback display
- Connectivity Impact: Client-side validation functions offline, reducing bandwidth dependency
Related Form Elements
Connected mobile validation components using semantic relationships:
- Associated Input Fields: All form controls benefit from immediate validation feedback
- Validation Patterns: Error handling mechanisms work alongside success indicators
- Navigation Controls: Form progression elements coordinate with validation state
- Accessibility Features: Screen readers announce validation changes through ARIA live regions
Implementation Requirements
Technical prerequisites for client-side validation:
- Browser compatibility across Safari, Chrome, and mobile browsers
- JavaScript methods: addEventListener, checkValidity(), setCustomValidity()
- HTML5 validation attributes: required, pattern, min, max
- CSS pseudo-classes: :valid, :invalid, :user-valid for styling feedback
Always Validate on the Server-Side for Security
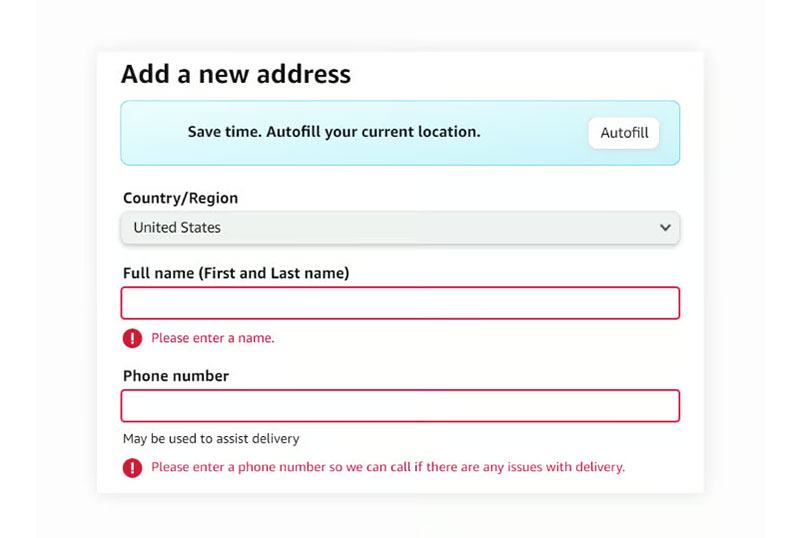
Image source: LogRocket
Server-side validation acts as the final security checkpoint for all form submissions. This validation method processes user data after transmission from the client browser, ensuring complete data integrity and preventing malicious inputs from reaching application databases. Unlike client-side validation, server-side checks cannot be bypassed by users.
Technical Specifications
Essential server-side validation requirements:
- Input Type: All data types require server validation regardless of client-side checks
- Touch Target Size: Not applicable for server processing
- Viewport Behavior: Error responses reload pages or update specific form sections
- Validation Method: On-submit validation with comprehensive data sanitization
User Experience Impact
Server-side validation provides critical security benefits while maintaining user experience:
- Input validation must be implemented on the server-side before any data is processed by application functions, as client-side validation can be circumvented
- Security improvements prevent SQL injection, XSS, and other attack vectors
- Data integrity maintenance ensures only valid information enters databases
- WCAG 2.1 AA compliance through proper error message presentation
Mobile-Specific Considerations
Server validation considerations for mobile contexts:
- Screen Size Adaptation: Server error pages must display properly on small screens
- Touch Interaction: Form resubmission requires clear touch targets after server validation
- Keyboard Optimization: Error correction maintains keyboard state and input focus
- Connectivity Impact: Server validation requires network connection, with appropriate loading states
Related Form Elements
Server-side validation integration points:
- Associated Input Fields: All input controls require corresponding server validation rules
- Validation Patterns: Server-side validation prevents common attacks like cross-site scripting (XSS) and SQL injection
- Navigation Controls: Form submission handling includes comprehensive error management
- Accessibility Features: Server error responses include proper ARIA attributes and focus management
Implementation Requirements
Technical specifications for secure server-side validation:
- Framework-specific validation libraries (Express Validator, Laravel Validation)
- Input sanitization methods: htmlspecialchars(), strip_tags(), prepared statements
- Security headers and CSRF token validation
- Error logging and monitoring for security incident detection
Provide Clear, Specific Error Messages
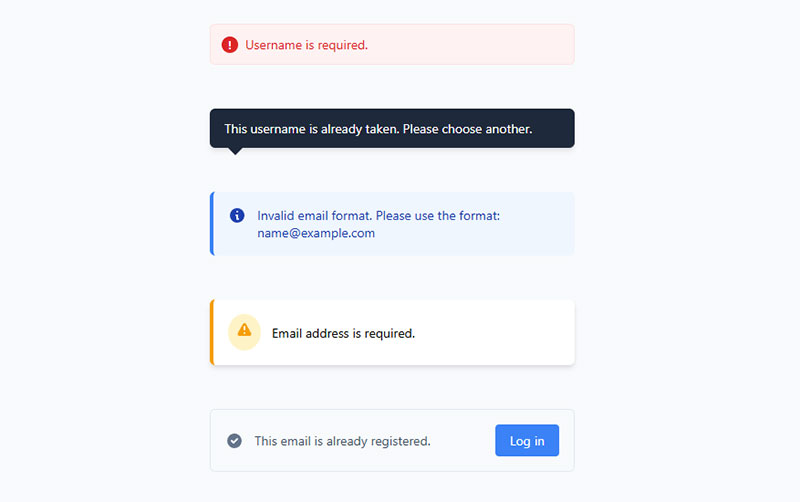
Clear error messages guide users toward successful form completion by explaining exactly what went wrong and how to fix issues. Effective error messaging uses specific, actionable language that helps users understand requirements without creating frustration. Message clarity directly impacts form abandonment rates and user satisfaction.
Technical Specifications
Error message implementation for mobile optimization:
- Input Type: Text messages with specific formatting requirements
- Touch Target Size: Error messages require adequate spacing for mobile readability
- Viewport Behavior: Messages appear without disrupting form layout or causing content shifts
- Validation Method: Context-sensitive error display based on field type and validation failure
User Experience Impact
Well-crafted error messages can reduce frustration and help keep users on track to complete their submissions, enhancing conversion rates. Performance metrics include:
- Removing a single field can boost form completion rate by 25% when combined with clear messaging
- Error correction time reduces when users understand specific requirements
- Form completion and conversion rates improve when error messages specify required actions
- Accessibility compliance improves through descriptive, screen-reader-friendly messages
Mobile-Specific Considerations
Mobile error message optimization factors:
- Screen Size Adaptation: Concise messaging fits mobile screen constraints while remaining informative
- Touch Interaction: Error messages position near relevant fields for easy correction
- Keyboard Optimization: Messages avoid triggering keyboard dismissal during error correction
- Connectivity Impact: Client-side error messages provide immediate feedback without network delays
Related Form Elements
Error message relationships within form structure:
- Associated Input Fields: Each field type requires tailored error messaging approaches
- Validation Patterns: Error content varies based on validation rule violations
- Navigation Controls: Error states affect form submission and navigation availability
- Accessibility Features: ARIA describedby attributes connect error messages to form fields
Implementation Requirements
Technical requirements for effective error messaging:
- Error messages should be explicit, human-readable, polite, precise, and give constructive advice
- Message positioning near form fields using CSS absolute or relative positioning
- JavaScript methods for dynamic message updates and removal
- Internationalization support for multi-language error content
Validate in Real-Time as Users Type
Real-time validation provides immediate feedback during user input, catching errors as they occur rather than after form submission. This validation approach monitors input changes and displays feedback dynamically, creating responsive user interactions. Real-time validation works best for immediate feedback on email validation and password validation.
Technical Specifications
Real-time validation technical requirements:
- Input Type: JavaScript event listeners on input, keyup, and blur events
- Touch Target Size: Validation feedback requires mobile-friendly touch targets for interaction
- Viewport Behavior: Dynamic messages avoid triggering viewport changes or zoom behavior
- Validation Method: Wait until the user exits the field (on blur) or types enough characters to trigger a check
User Experience Impact
Real-time validation performance benefits:
- Live validation can boost user confidence and create a sense of progression with green checkmarks
- The amount of time needed to correct errors decreases significantly, as input context remains fresh in user’s mind
- Error prevention improves through immediate feedback on password strength and format requirements
- Mobile typing efficiency increases when users receive confirmation of correct input
Mobile-Specific Considerations
Real-time validation mobile optimization:
- Screen Size Adaptation: Feedback messages size appropriately for mobile viewport constraints
- Touch Interaction: Overly aggressive premature validation negatively impacts experience as users are told their input is wrong before they have had a chance to type correctly
- Keyboard Optimization: Validation timing avoids interrupting mobile typing flow
- Connectivity Impact: Client-side real-time validation functions without network dependency
Related Form Elements
Real-time validation component relationships:
- Associated Input Fields: Password fields, email inputs, and username fields benefit most from real-time feedback
- Validation Patterns: Password strength meters and username availability checks work well with live validation
- Navigation Controls: Form progression indicators update based on real-time validation status
- Accessibility Features: Screen readers announce validation changes through ARIA live regions
Implementation Requirements
Technical implementation for real-time validation:
- JavaScript debouncing to prevent excessive validation calls during rapid typing
- Event handling for input, blur, and focus events across different input types
- CSS transitions for smooth feedback appearance and removal
- Performance optimization to prevent validation lag on slower mobile devices
Use Appropriate Input Types (Email, Tel, Number)
Appropriate HTML5 input types trigger optimized mobile keyboards and provide built-in validation constraints. These specialized input types improve data entry efficiency by presenting relevant keyboard layouts and preventing common input errors. Touch devices with dynamic keyboards present different virtual keypads that are more suitable for specific input types.
Technical Specifications
HTML5 input type specifications for mobile optimization:
- Input Type: email, tel, number, url, date with specific keyboard triggers
- Touch Target Size: Input fields require 44px × 44px minimum dimensions
- Viewport Behavior: Mobile browsers may present custom keypads optimized for entering specific data types
- Validation Method: Built-in browser validation combined with pattern attributes
User Experience Impact
Input type optimization measurable improvements:
- Data entry speed increases through appropriate keyboard presentation
- Error reduction occurs when input types prevent invalid character entry
- Email input type provides built-in client-side error validation performed by browser before server submission
- Mobile usability improves through context-appropriate keyboard layouts
Mobile-Specific Considerations
Mobile input type optimization factors:
- Screen Size Adaptation: Specialized keyboards maximize available input space
- Touch Interaction: Tel input type causes mobile browsers to display special keyboard for entering phone numbers
- Keyboard Optimization: Number inputs show numeric keypads, email shows @ symbol access
- Connectivity Impact: Input type validation occurs client-side without network requirements
Related Form Elements
Input type relationships with validation systems:
- Associated Input Fields: Each input type pairs with specific validation patterns and constraints
- Validation Patterns: Email patterns, phone number formats, and numeric ranges work with input types
- Navigation Controls: Form completion rates improve with appropriate input type selection
- Accessibility Features: Screen readers announce input type expectations to users
Implementation Requirements
Technical requirements for input type implementation:
- HTML5 input type attributes: type=”email”, type=”tel”, type=”number”
- Pattern attributes for additional format constraints beyond basic type validation
- Fallback handling for older browsers that don’t support HTML5 input types
- Testing across different mobile browsers and keyboard implementations
Implement Proper Password Strength Requirements
See the Pen
Password strength checker by Coding Beast (@coding_beast)
on CodePen.
Password strength requirements guide users toward creating secure passwords while providing clear feedback about security criteria. Effective password validation displays requirements prominently and updates feedback as users type. Strong password policies balance security needs with user experience considerations.
Technical Specifications
Password validation technical specifications:
- Input Type: Password input with real-time strength indicators and requirement lists
- Touch Target Size: Password visibility toggles and requirement indicators need 44px minimum
- Viewport Behavior: Password requirements display without triggering viewport changes
- Validation Method: Real-time validation with visual progress indicators for each requirement
User Experience Impact
Password strength validation user benefits:
- Security improvements through enforced password complexity requirements
- Real-time feedback makes it easier for users to check compliance with password requirements
- User confidence increases with clear progress indication during password creation
- Account security enhances without creating excessive user friction
Mobile-Specific Considerations
Mobile password validation considerations:
- Screen Size Adaptation: Password requirements list displays efficiently on small screens
- Touch Interaction: Password visibility toggles accommodate touch-based interaction patterns
- Keyboard Optimization: Secure keyboard input prevents password visibility in suggestions
- Connectivity Impact: Password strength checking occurs client-side for immediate feedback
Related Form Elements
Password validation component relationships:
- Associated Input Fields: Password confirmation fields coordinate with strength requirements
- Validation Patterns: Regex patterns enforce character combinations and length requirements
- Navigation Controls: Form security improvements affect overall form submission flow
- Accessibility Features: Screen readers announce password requirement completion status
Implementation Requirements
Technical implementation for password strength validation:
- JavaScript password strength algorithms evaluating length, complexity, and common patterns
- CSS styling for requirement progress indicators and strength meters
- Regular expressions for character type validation (uppercase, lowercase, numbers, symbols)
- Security considerations preventing password data exposure in client-side validation
Sanitize and Escape All User Inputs
Input sanitization removes or neutralizes potentially malicious content from user submissions before data processing occurs. This security measure prevents code injection attacks and ensures data integrity throughout application workflows. Proper sanitization works alongside validation to create comprehensive input security.
Technical Specifications
Input sanitization technical requirements:
- Input Type: All text, numeric, and file inputs require sanitization processing
- Touch Target Size: Not applicable for backend sanitization processes
- Viewport Behavior: Sanitization occurs server-side without affecting user interface
- Validation Method: Multi-layer sanitization before and after validation processes
User Experience Impact
Input sanitization security benefits:
- Sanitization prevents common attacks like cross-site scripting (XSS) and SQL injection
- Data integrity improvements ensure consistent, clean data storage
- Application stability increases through malicious input prevention
- User trust improves through demonstrated security practices
Mobile-Specific Considerations
Mobile sanitization implementation factors:
- Screen Size Adaptation: Error messages for sanitization issues display appropriately on mobile
- Touch Interaction: Sanitization processes don’t interfere with mobile form interaction
- Keyboard Optimization: Input sanitization maintains keyboard state during processing
- Connectivity Impact: Server-side sanitization requires network connectivity for processing
Related Form Elements
Sanitization integration with form components:
- Associated Input Fields: All form inputs require corresponding sanitization rules
- Validation Patterns: Sanitization complements validation without replacing security checks
- Navigation Controls: Form submission handling includes sanitization processing steps
- Accessibility Features: Sanitization error messages maintain accessibility standards
Implementation Requirements
Technical specifications for input sanitization:
- HTML encoding returns malicious data like <script> as <script>
- Backend sanitization libraries: DOMPurify, HTMLPurifier, or framework-specific tools
- Content Security Policy (CSP) headers for additional XSS protection
- Regular security audits and sanitization rule updates
Use HTTPS for Sensitive Data Transmission
HTTPS encryption protects sensitive form data during transmission between user devices and servers. This security protocol prevents data interception and ensures user privacy during form submissions. All forms handling personal information, login credentials, or payment data require HTTPS implementation.
Technical Specifications
HTTPS implementation requirements for forms:
- Input Type: All form inputs benefit from encrypted transmission
- Touch Target Size: HTTPS doesn’t affect form element sizing requirements
- Viewport Behavior: Secure connections load without affecting mobile viewport behavior
- Validation Method: HTTPS works alongside all validation methods without interference
User Experience Impact
HTTPS security user benefits:
- Data privacy protection during form submission processes
- User trust increases through visible security indicators in browser address bars
- Compliance with security standards and regulations (GDPR, PCI-DSS)
- SEO benefits as search engines prioritize HTTPS websites
Mobile-Specific Considerations
Mobile HTTPS implementation considerations:
- Screen Size Adaptation: Security indicators display appropriately on mobile browsers
- Touch Interaction: Encrypted connections don’t affect mobile form usability
- Keyboard Optimization: HTTPS maintains keyboard functionality across secure connections
- Connectivity Impact: SSL handshake adds minimal latency on modern mobile networks
Related Form Elements
HTTPS integration with form security:
- Associated Input Fields: All sensitive inputs require encrypted transmission protection
- Validation Patterns: HTTPS complements validation security without replacing other measures
- Navigation Controls: Secure form submission maintains HTTPS throughout the process
- Accessibility Features: Security features don’t impact accessibility compliance
Implementation Requirements
Technical requirements for HTTPS implementation:
- Valid SSL/TLS certificates from trusted certificate authorities
- Server configuration for HTTPS-only form submission endpoints
- HTTP to HTTPS redirects for all form-containing pages
- Security headers: HSTS, secure cookie flags, and CSP implementation
Set Appropriate Field Length Limits
Field length limitations prevent system abuse and maintain data quality by restricting input to reasonable character counts. These constraints protect against buffer overflow attacks while ensuring consistent data storage requirements. Proper field sizing also provides visual cues to users about expected input length, improving form completion accuracy.
Technical Specifications
Essential field length attributes for mobile optimization:
- Input Type: maxlength and minlength attributes on text, email, url, tel inputs
- Touch Target Size: Input fields require 44px × 44px minimum for mobile interaction
- Viewport Behavior: Field width should match expected input length for visual consistency
- Validation Method: Client-side length checking combined with server-side enforcement
User Experience Impact
Appropriate field length limits provide measurable benefits:
- The length of an input field should be in proportion to the amount of information expected in the field
- User expectations improve when field width visually indicates required input length
- Data quality increases through prevention of excessive or insufficient input
- Form completion rates improve when users understand input requirements clearly
Mobile-Specific Considerations
Mobile field length optimization factors:
- Screen Size Adaptation: Field widths adjust proportionally to mobile screen constraints
- Touch Interaction: Longer fields may require horizontal scrolling considerations
- Keyboard Optimization: Character count displays help users stay within limits
- Connectivity Impact: Client-side length limits reduce unnecessary server requests
Related Form Elements
Field length relationships with form components:
- Associated Input Fields: Username, zip codes, and phone numbers require specific length constraints
- Validation Patterns: Character limits work alongside format validation for complete input control
- Navigation Controls: Form progression depends on meeting length requirements
- Accessibility Features: Screen readers announce character limits when properly implemented
Implementation Requirements
Technical requirements for field length implementation:
- HTML attributes: maxlength=”50″ minlength=”3″ for input elements
- JavaScript validation for real-time character counting and feedback
- CSS styling for field width matching expected content length
- Server-side validation to enforce length limits regardless of client-side bypassing
Validate File Uploads for Type and Size
File upload validation prevents security vulnerabilities by checking file types, sizes, and content before processing. This validation includes examining file extensions, MIME types, and file signatures to ensure only safe files reach server systems. Comprehensive file validation protects against malware uploads, resource exhaustion attacks, and unauthorized file execution.
Technical Specifications
File validation technical requirements for mobile security:
- Input Type: File input elements with accept attribute restrictions
- Touch Target Size: File upload buttons need 44px minimum dimensions for touch accessibility
- Viewport Behavior: Upload progress indicators display appropriately on mobile screens
- Validation Method: Multi-layer validation including extension, MIME type, and file signature checking
User Experience Impact
File upload security validation benefits:
- Set the files permissions on the principle of least privilege
- Security improvements prevent malware and malicious script uploads
- Server resource protection through file size limitations preventing DoS attacks
- Data integrity maintenance by ensuring only expected file types are processed
Mobile-Specific Considerations
Mobile file upload validation considerations:
- Screen Size Adaptation: Error messages for invalid files display clearly on small screens
- Touch Interaction: File selection interfaces accommodate touch-based file browsing
- Keyboard Optimization: File upload validation doesn’t interfere with mobile file selection
- Connectivity Impact: Large file validation may require progress indicators for slower connections
Related Form Elements
File upload validation component relationships:
- Associated Input Fields: File upload forms often include description and category fields
- Validation Patterns: File type validation works alongside size and content security checks
- Navigation Controls: File upload security affects form submission and processing workflows
- Accessibility Features: Screen readers announce file validation errors and requirements
Implementation Requirements
Technical specifications for secure file upload validation:
- List allowed extensions. Only allow safe and critical extensions for business functionality
- File signature validation comparing against known safe file types
- Server-side file scanning with antivirus integration when possible
- Content type verification beyond trusting client-provided MIME types
Use CSRF Tokens to Prevent Cross-Site Attacks
CSRF tokens prevent cross-site request forgery attacks by including unique, unpredictable tokens in form submissions. These tokens verify that requests originate from authenticated users rather than malicious third-party sites. Each form submission requires a valid token that matches the user’s session, making unauthorized requests impossible without token access.
Technical Specifications
CSRF protection implementation requirements:
- Input Type: Hidden input fields containing cryptographically secure random tokens
- Touch Target Size: CSRF tokens don’t affect user interface elements directly
- Viewport Behavior: Hidden token fields have no visual impact on mobile displays
- Validation Method: Server-side token verification on every state-changing request
User Experience Impact
CSRF token security advantages:
- CSRF tokens prevent CSRF because without a CSRF token, an attacker cannot create valid requests to the backend server
- Security enhancement protects user accounts from unauthorized actions
- Session integrity maintenance prevents account hijacking through forged requests
- User trust increases through demonstrated protection against common web attacks
Mobile-Specific Considerations
Mobile CSRF token implementation factors:
- Screen Size Adaptation: CSRF protection operates invisibly without affecting mobile interfaces
- Touch Interaction: Token validation doesn’t interfere with mobile form submission flows
- Keyboard Optimization: CSRF tokens have no impact on mobile keyboard interactions
- Connectivity Impact: Token validation adds minimal overhead to form submissions
Related Form Elements
CSRF token integration with form security:
- Associated Input Fields: All state-changing forms require CSRF token protection
- Validation Patterns: CSRF tokens complement other security measures without replacement
- Navigation Controls: Form submission security depends on valid token inclusion
- Accessibility Features: CSRF protection maintains form accessibility without additional requirements
Implementation Requirements
Technical requirements for CSRF token implementation:
- The CSRF token can be transmitted to the client as part of a response payload, such as a HTML or JSON response
- Cryptographically secure random token generation for each user session
- Server-side token validation on all POST, PUT, PATCH, and DELETE requests
- Token regeneration after successful authentication and sensitive operations
Implement Rate Limiting to Prevent Spam
Rate limiting controls the frequency of form submissions to prevent automated spam attacks and resource abuse. This technique restricts the number of requests from individual IP addresses or user accounts within specified time windows. Rate limiting protects server resources while maintaining accessibility for legitimate users.
Technical Specifications
Rate limiting technical implementation:
- Input Type: Rate limiting applies to all form submission endpoints regardless of input types
- Touch Target Size: Rate limiting doesn’t affect form element sizing requirements
- Viewport Behavior: Rate limit notifications display appropriately on mobile screens
- Validation Method: Server-side request frequency monitoring with configurable thresholds
User Experience Impact
Rate limiting spam prevention benefits:
- Rate limiting is often employed to stop bad bots from negatively impacting a website or application
- Server performance improvement through prevention of resource exhaustion attacks
- Data quality enhancement by reducing spam submissions in forms and databases
- User experience protection by maintaining site responsiveness under attack conditions
Mobile-Specific Considerations
Mobile rate limiting implementation considerations:
- Screen Size Adaptation: Rate limit messages display clearly on mobile devices
- Touch Interaction: Rate limiting doesn’t interfere with normal mobile form usage
- Keyboard Optimization: Rate limits maintain mobile keyboard functionality
- Connectivity Impact: Rate limiting helps manage server load during high-traffic periods
Related Form Elements
Rate limiting relationships with form components:
- Associated Input Fields: All form inputs benefit from rate limiting protection
- Validation Patterns: Rate limiting works alongside other spam prevention measures
- Navigation Controls: Form submission rates affect overall site navigation performance
- Accessibility Features: Rate limiting maintains form accessibility while providing security
Implementation Requirements
Technical specifications for rate limiting implementation:
- Rate limiting is based on tracking the IP addresses that requests are coming from, and tracking how much time elapses between each request
- Configurable rate limits based on IP address, user account, and session
- Redis or similar caching systems for efficient rate limit tracking
- Progressive penalties increasing restriction duration for repeat violations
Provide Visual Indicators for Required Fields
Visual indicators for required fields help users identify mandatory form elements before submission, reducing errors and improving completion rates. These indicators must be accessible to all users, including those using screen readers or having visual impairments. Proper implementation combines visual cues with programmatic indicators for comprehensive accessibility.
Technical Specifications
Required field indicator technical requirements:
- Input Type: Visual indicators apply to all input types requiring user completion
- Touch Target Size: Required field indicators need sufficient size for mobile visibility
- Viewport Behavior: Indicators remain visible and clear on mobile screen sizes
- Validation Method: Combined visual and programmatic indicators using HTML5 and ARIA attributes
User Experience Impact
Required field visual indication benefits:
- Clearly indicating a required field improves form usability, helps users complete forms accurately, and ensures compliance with accessibility standards
- Error reduction through clear communication of mandatory fields before submission
- Form completion time improvement when users understand requirements upfront
- Accessibility compliance meeting WCAG 2.1 AA standards for inclusive design
Mobile-Specific Considerations
Mobile required field indicator optimization:
- Screen Size Adaptation: Indicators scale appropriately for mobile viewport constraints
- Touch Interaction: Required field indicators don’t interfere with touch-based input
- Keyboard Optimization: Indicators remain visible during mobile keyboard interactions
- Connectivity Impact: Visual indicators function without network dependencies
Related Form Elements
Required field indicator relationships:
- Associated Input Fields: All mandatory form controls need consistent visual treatment
- Validation Patterns: Required indicators complement error messaging and validation feedback
- Navigation Controls: Clear requirements improve form progression and completion rates
- Accessibility Features: Accessible forms require both visual and programmatic required field indicators
Implementation Requirements
Technical requirements for required field indicators:
- Using an asterisk to mark required fields is an easy way to improve the usability of your forms
- HTML5 required attribute and aria-required=”true” for programmatic indication
- Visual indicators like asterisks (*) with explanatory text for meaning clarification
- Consistent indicator placement and styling across all form elements
Test With Screen Readers for Accessibility
Screen reader testing ensures form validation works properly with assistive technologies used by visually impaired users. This testing verifies that validation messages, field labels, and error states are properly announced by screen reading software. Regular accessibility testing prevents exclusion of users who depend on assistive technologies for web navigation.
Technical Specifications
Screen reader testing technical requirements:
- Input Type: All form input types require screen reader compatibility testing
- Touch Target Size: Screen reader testing doesn’t affect touch target requirements
- Viewport Behavior: Screen reader testing covers mobile screen reader functionality
- Validation Method: Testing validation message announcement and field state communication
User Experience Impact
Screen reader accessibility testing benefits:
- Screen readers like NVDA, JAWS, and VoiceOver read form labels, instructions, and error messages aloud
- Accessibility compliance ensuring legal requirement adherence
- User base expansion through inclusion of visually impaired users
- Form usability improvement for all users through better semantic structure
Mobile-Specific Considerations
Mobile screen reader testing considerations:
- Screen Size Adaptation: Mobile screen readers require specific testing approaches
- Touch Interaction: Screen reader testing covers touch gesture compatibility
- Keyboard Optimization: Alternative navigation methods need verification with assistive technologies
- Connectivity Impact: Screen reader functionality testing across different connection speeds
Related Form Elements
Screen reader testing component coverage:
- Associated Input Fields: All form controls need screen reader compatibility verification
- Validation Patterns: Error messages and feedback require assistive technology testing
- Navigation Controls: Form progression must work with screen reader navigation
- Accessibility Features: Comprehensive testing covers ARIA attributes and semantic HTML
Implementation Requirements
Technical requirements for screen reader testing:
- They rely on semantic HTML and WAI-ARIA attributes to understand form structure
- Testing with multiple screen readers including NVDA, JAWS, and VoiceOver
- Automated accessibility testing tools integrated into development workflow
- Manual testing procedures covering form completion scenarios with assistive technologies
Use Regex Patterns for Format Validation
Regular expression patterns provide precise format validation for structured data inputs like phone numbers, email addresses, and postal codes. Regex validation ensures data consistency while providing immediate feedback to users about formatting requirements. These patterns work client-side for instant validation and server-side for security enforcement.
Technical Specifications
Regex pattern validation technical implementation:
- Input Type: Pattern attribute works with text, email, tel, url, and password input types
- Touch Target Size: Pattern validation doesn’t affect mobile touch target requirements
- Viewport Behavior: Pattern validation error messages display appropriately on mobile
- Validation Method: HTML5 pattern attribute combined with JavaScript for enhanced feedback
User Experience Impact
Regex format validation advantages:
- The pattern attribute specifies a regular expression that defines a pattern the entered data needs to follow
- Data quality improvement through consistent formatting enforcement
- User guidance through clear format expectations and validation feedback
- Error prevention by catching format issues during input rather than after submission
Mobile-Specific Considerations
Mobile regex validation optimization:
- Screen Size Adaptation: Format validation messages fit mobile screen constraints
- Touch Interaction: Pattern validation works seamlessly with mobile input methods
- Keyboard Optimization: Appropriate keyboards trigger for different input patterns
- Connectivity Impact: Client-side pattern validation provides immediate feedback without server requests
Related Form Elements
Regex pattern validation relationships:
- Associated Input Fields: Email, phone, and postal code fields benefit most from pattern validation
- Validation Patterns: Regex patterns complement other validation methods for comprehensive input checking
- Navigation Controls: Format validation prevents form submission with incorrectly formatted data
- Accessibility Features: Pattern validation includes accessible error messaging for screen readers
Implementation Requirements
Technical specifications for regex pattern implementation:
- HTML5 pattern attribute with appropriate regular expressions for data types
- JavaScript validation for real-time pattern matching and user feedback
- Server-side pattern validation for security and data integrity enforcement
- User-friendly error messages explaining format requirements and providing examples
FAQ on Form Validation Best Practices
What’s the difference between client-side and server-side validation?
Client-side validation provides instant feedback in the browser before form submission. Server-side validation processes data after transmission to prevent security vulnerabilities.
Both work together. Client-side improves user experience while server-side ensures data integrity and prevents malicious attacks like SQL injection.
When should I show validation error messages?
Show error messages after users finish typing in a field (on blur). Avoid premature validation that appears while users are still entering data.
Real-time validation works best for complex fields like passwords. Wait until input is complete before displaying feedback to prevent user frustration.
How do I write effective form error messages?
Be specific and actionable. Instead of “Invalid input,” write “Enter a valid email address ([email protected]).” Tell users exactly what went wrong and how to fix it.
Use friendly, conversational language. Avoid technical jargon that confuses users and increases form abandonment rates.
Should I use HTML5 validation or JavaScript validation?
Use both for optimal results. HTML5 validation provides fast, built-in constraints while JavaScript offers customization and better error handling.
Start with robust HTML5 features like required and pattern attributes. Then enhance the user experience with JavaScript for dynamic feedback and styling.
What input types work best on mobile devices?
Use appropriate HTML5 input types: email, tel, number, and url. These trigger optimized mobile keyboards that improve data entry speed.
Touch targets should be at least 44px × 44px. Mobile browsers display custom keypads for telephone numbers and email addresses automatically.
How can I prevent form spam and security attacks?
Implement server-side validation for all inputs, use HTTPS for data transmission, and sanitize user inputs before processing. Add CSRF tokens to prevent cross-site attacks.
Rate limiting helps prevent spam submissions. Never trust client-side validation alone as users can bypass JavaScript restrictions easily.
What’s the best way to validate passwords?
Show password requirements clearly and provide real-time feedback as users type. Include minimum length, character combinations, and strength indicators.
Use password strength meters that update dynamically. Allow users to toggle password visibility and confirm passwords match without excessive friction.
How do I make form validation accessible?
Use ARIA labels and describedby attributes to connect error messages with form fields. Ensure error messages are announced by screen readers.
Don’t rely on color alone for validation feedback. Include icons, text, and proper focus management for users with disabilities.
Should I validate forms in real-time or after submission?
Inline validation works best for immediate feedback on email inputs and password fields. Use after-submission validation for complex forms with many fields.
Hybrid approaches combine both methods. Real-time validation for critical fields, comprehensive validation on submission for complete error checking.
What are common form validation mistakes to avoid?
Avoid generic error messages, premature validation, and validation that disrupts typing flow. Don’t disable form submission buttons before users attempt to submit.
Skip validation for optional fields unless users enter data. Test with real users to identify friction points and improve completion rates.
Conclusion
Implementing form validation best practices transforms user interactions from frustrating obstacles into smooth experiences. Data validation protects your systems while validation UX patterns guide users toward successful completion.
Cross-browser validation ensures consistency across platforms. Custom validators handle unique business requirements while maintaining security standards.
Validation performance matters for mobile forms where users expect instant responses. Bootstrap and modern CSS frameworks simplify validation styling while Angular, React, and Vue.js offer powerful validation ecosystems.
Great validation happens invisibly. Users complete forms without thinking about rules or restrictions while field validation guides naturally.
Your forms should work flawlessly whether users access them through Chrome DevTools during development or on mobile devices in poor network conditions. Error handling feels supportive rather than critical when implemented correctly.
Start implementing these validation strategies today. Your users will thank you with higher engagement, fewer support tickets, and improved conversion rates across all device types.