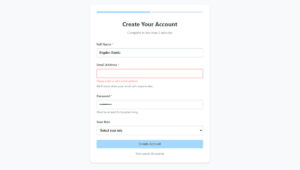
Spam bots submitted over 99 billion junk form entries across the web in 2024. Your site caught some of that traffic, guaranteed. The best tactics for form spam prevention combine…
Table of Contents
Your form gets traffic but barely any submissions. Frustrating, right?
Most businesses lose 70% of potential conversions because their forms create unnecessary friction. Users abandon at the smallest obstacle: too many fields, confusing labels, slow loading times.
Learning how to optimize forms for better conversions directly impacts your bottom line. Small changes to field count, button copy, or validation timing can double your completion rates.
This guide covers proven strategies across form field reduction, mobile optimization, trust signals, error handling, and analytics. You’ll discover exactly which elements destroy conversion rates and how to fix them.
Stop losing leads to poorly designed forms.
Form Field Reduction Strategies
Forms with fewer fields convert better. Period.
Each additional field creates another decision point where users can abandon. Research shows removing just one unnecessary field can boost conversions by 10-15%.
Audit Current Fields
Review every field in your forms. Ask: is this information absolutely necessary right now?
Many businesses request data they don’t immediately need. That’s a conversion killer.
Combine Related Fields
Instead of separate fields for first name and last name, use a single “Full Name” field when legal names aren’t required.
Address fields can often merge into fewer inputs. Phone and extension? One field with proper formatting.
Use Progressive Disclosure
Don’t show all form fields at once. Reveal additional inputs based on previous answers.
Conditional logic displays relevant fields only when needed, keeping forms shorter and less intimidating.
Smart Defaults and Pre-filling
Auto-populate fields whenever possible. Country selection, time zones, or industry categories with intelligent defaults reduce mental load.
Browser autofill and saved data make completion faster, especially on mobile forms.
Required vs Optional Field Strategy
Mark optional fields clearly instead of marking everything required.
Better yet, remove optional fields entirely. If you don’t need it now, ask later.
Form Layout and Visual Hierarchy
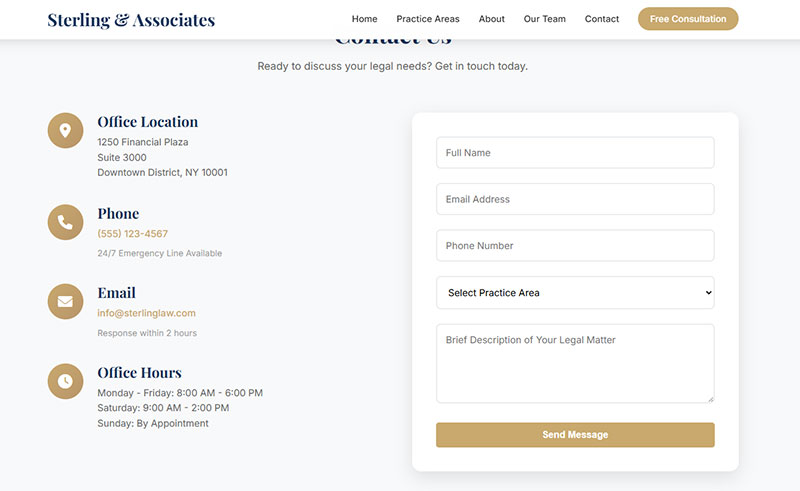
Single-column layouts outperform multi-column designs in most tests.
Users can scan vertically faster than jumping between columns, reducing cognitive effort and completion time.
Single Column Design Benefits
One clear path forward eliminates confusion about where to look next.
Multi-column forms work for very short forms (3-4 fields max) or when grouping clearly related data like address components.
Field Spacing and White Space
Cramped forms feel overwhelming. Proper spacing between fields improves visual clarity and reduces errors.
Aim for 15-20 pixels between fields, more between logical groups.
Visual Grouping Techniques
Related fields should sit close together with clear separation from other groups.
Use subtle background shading, borders, or extra spacing to define sections without cluttering the design.
Label Placement Options
Top-aligned labels convert best across devices. They’re fastest to scan and work perfectly on mobile screens.
Left-aligned labels work for familiar forms where users know what to expect. Avoid right-aligned labels entirely.
Inline labels (inside fields) save space but disappear when users type, potentially causing confusion.
Button Position and Prominence
Submit buttons belong left-aligned with form fields, not centered.
Left alignment follows the natural reading pattern and feels like the next step in the flow.
Make the primary action button stand out with size and color. Secondary actions (like “Cancel”) should be less prominent.
Form Field Labels and Instructions
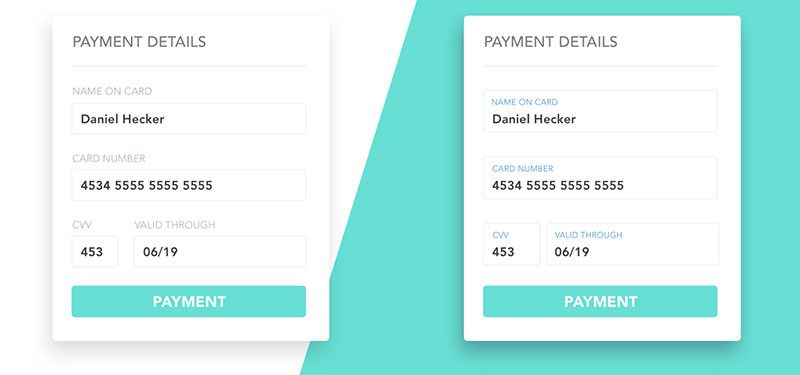
Image source: UX Planet
Clear labels prevent errors and speed up completion.
Ambiguous language forces users to guess what you want, leading to mistakes and abandonment.
Write Descriptive Labels
“Email” is clearer than “Email Address” (users know). “Work Email” is better when you need a specific type.
Skip cute or clever wording. “Where should we send your goodies?” is worse than “Shipping Address.”
Effective Microcopy Usage
Brief helper text below fields clarifies expectations without cluttering labels.
“We’ll never share your email” or “Used for order updates only” builds trust right where users need it.
Placeholder Text Best Practices
Placeholder text should show format examples, not replace labels.
“[email protected]” demonstrates email format. “Enter your email” just repeats the label and disappears when typing starts.
Never use placeholders as the only label. Accessibility suffers and users forget what the field wants.
Inline Validation Messages
Real-time form validation catches errors immediately, before submission.
Validate on blur (when users leave a field) rather than on every keystroke. Immediate keystroke validation feels aggressive and interrupts flow.
Error Message Clarity
Generic “Invalid input” messages frustrate users. Explain exactly what’s wrong and how to fix it.
“Password must include at least 8 characters, one number, and one special character” beats “Invalid password” every time.
Position error messages directly next to or below the problematic field with clear visual indicators.
Mobile Form Optimization
More than 60% of form submissions happen on mobile devices.
Desktop-first forms destroy mobile conversion rates through tiny tap targets, awkward keyboards, and endless scrolling.
Touch Target Sizing
Buttons and input fields need minimum 44×44 pixel tap targets.
Smaller targets cause frustration and errors as users struggle to hit the right field.
Appropriate Keyboard Types
The right keyboard appears automatically when input types match field purposes.
type="email" shows the email keyboard with @ symbol. type="tel" displays the number pad. type="number" works for quantities.
Getting this wrong forces users to switch keyboards manually. That’s friction you can’t afford.
Autofill and Autocomplete Support
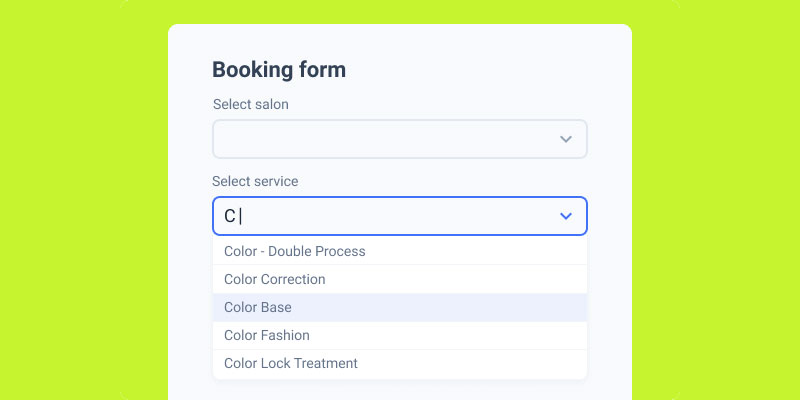
Image source: JetFormBuilder
Mobile typing is slow and error-prone. Browser autofill speeds up completion dramatically.
Use proper autocomplete attributes: autocomplete="name", autocomplete="email", autocomplete="tel".
Responsive Design Considerations
Forms must adapt to different screen sizes without breaking layout or hiding elements.
Test on actual devices, not just browser resize. Touch interactions behave differently than mouse clicks.
Stack fields vertically on small screens even if your desktop version uses columns.
Form Loading Speed and Performance
Slow forms kill conversions before users even start filling them out.
Every second of delay reduces completion rates. Forms loading in under 2 seconds convert 30% better than those taking 5+ seconds.
Optimize Form Scripts
Heavy JavaScript libraries bloat page weight unnecessarily.
Load only the validation and interaction scripts you actually need. Defer non-critical scripts until after the form renders.
Reduce External Dependencies
Each third-party service adds loading time and potential failure points.
Analytics trackers, chat widgets, and social media buttons can wait until after form submission.
Lazy Load Form Elements
Load visible fields first, additional sections on scroll or interaction.
Multi-step forms naturally spread the load across pages, improving perceived performance.
Image and Asset Optimization
Icons and decorative elements should be SVG when possible, optimized PNGs otherwise.
Background images rarely add enough value to justify their file size on forms.
Autofill and Input Assistance
Users hate retyping information browsers already know.
Proper autofill implementation can cut completion time by 50% or more.
Browser Autofill Configuration
Use standard HTML autocomplete attributes so browsers recognize field purposes.
autocomplete="given-name", autocomplete="family-name", autocomplete="street-address" trigger saved data automatically.
Autocomplete Attribute Usage
Match attributes to actual field purposes, not generic “on/off” values.
Wrong attributes prevent autofill from working. No attributes mean users type everything manually.
Input Masks and Formatting
Format phone numbers, credit cards, and dates automatically as users type.
(555) 123-4567 is easier to verify than 5551234567. Real-time formatting reduces errors and builds confidence.
Predictive Text Implementation
Suggest common responses for fields like job titles, company names, or cities.
Address autocomplete using postal service APIs saves massive time and prevents shipping errors.
Form Trust Signals
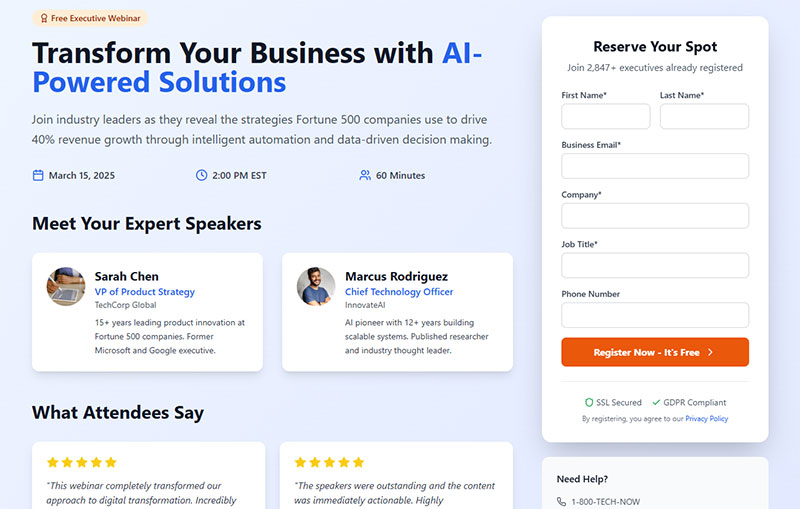
Users won’t complete forms they don’t trust.
Security indicators and privacy assurances directly impact conversion rates, especially for lead generation forms requesting personal data.
Security Badge Placement
SSL certificates and security seals belong near submit buttons where decision-making happens.
Position trust indicators where users look right before committing. Above the fold matters less than near the action.
Privacy Statement Integration
Brief privacy notices should appear directly on the form.
“We respect your privacy. Read our policy” with a link beats hiding privacy details on a separate page users won’t visit.
HTTPS Visual Indicators
Padlock icons in the address bar aren’t enough anymore.
Mention encryption explicitly: “Your information is encrypted and secure.”
Data Protection Notices
GDPR compliant forms require clear consent language and checkboxes for data processing.
Vague “By submitting, you agree to our terms” doesn’t meet legal requirements or build trust.
Progress Indicators for Multi-Step Forms
Show users exactly where they are in the process and how much remains.
Step counters (“Step 2 of 4”) or progress bars reduce abandonment by setting clear expectations.
Form Button Design and Copy
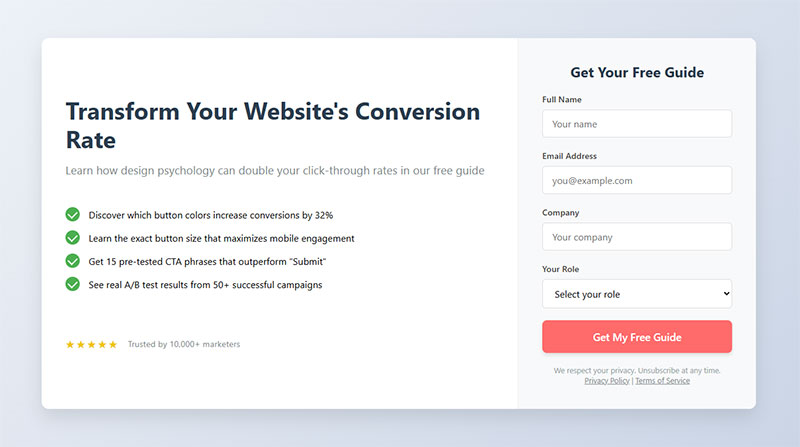
Your submit button determines whether users complete or abandon at the last second.
Generic “Submit” buttons convert 20-30% worse than specific, action-oriented alternatives.
Action-Oriented Button Text
“Get My Free Guide” outperforms “Submit” by clearly stating the benefit.
“Start My Trial,” “Download Now,” or “Book My Appointment” tell users exactly what happens next.
Button Color and Contrast
Primary buttons need high contrast against background colors.
Test your button in grayscale. If it doesn’t stand out, it won’t work in color either.
Button Size and Positioning
Make buttons big enough to be obvious, small enough to feel proportional.
44 pixels minimum height for mobile, 36-40 pixels for desktop. Full-width buttons work well on mobile, fixed-width on desktop.
Call-to-Action Clarity
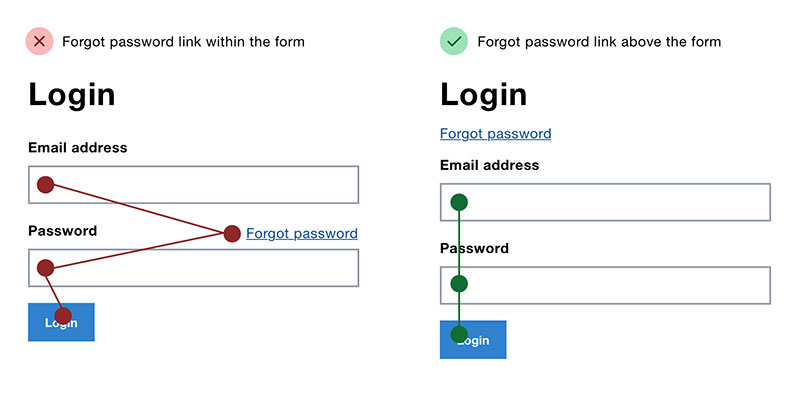
Image source: Adam Silver
Remove doubt about what happens when users click.
Ambiguous CTAs like “Continue” or “Next” don’t specify the outcome. “Send My Quote” or “Create Account” do.
Multi-Step Form Optimization
Breaking long forms into steps increases completion rates when done right.
Single-step forms vs multi-step forms each have advantages depending on context and field count.
When to Use Multi-Step Forms
Forms with 7+ fields benefit from splitting into logical sections.
Complex forms feel less overwhelming when divided. Registration, checkout, and detailed applications work well as multi-step.
Step Organization Logic
Group related fields together in each step.
Personal info, then address, then payment makes sense. Random field order across steps confuses users and breaks flow.
Progress Indicator Design
Visual progress bars show completion percentage, step numbers show finite stages.
“Step 2 of 4” feels more achievable than “50% complete” for the same position.
Save and Resume Functionality
Long application or intake forms need the ability to save progress.
Email a unique link users can return to later. Losing 20 minutes of work guarantees they won’t start over.
Step Navigation Best Practices
Allow backward navigation to fix mistakes without restarting.
“Back” and “Next” buttons should both be visible. Don’t trap users moving only forward.
Form Error Handling
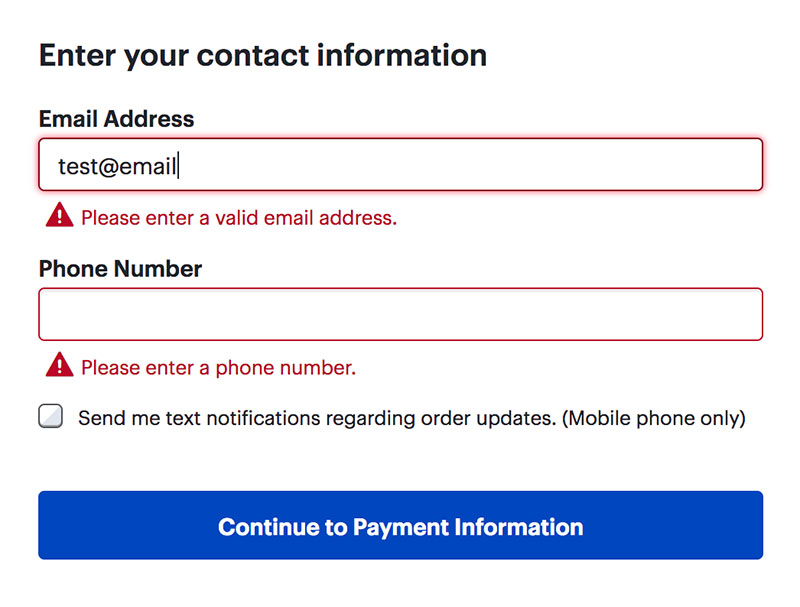
Image source: Nielsen Norman Group
How you handle mistakes determines whether users fix them or leave.
Waiting until submission to show errors is the worst possible approach.
Inline Validation Timing
Validate when users leave a field (onBlur), not on every keystroke.
Keystroke validation while typing feels aggressive and interrupts thought. Wait until they’re done with that field.
Error Message Positioning
Place error text immediately below or beside the problematic field with a red indicator.
Errors at the top of the form force users to hunt for the actual problem.
Error Message Tone
Explain what’s wrong without sounding accusatory.
“Please enter a valid email address” beats “Error: Invalid input.” Helpful tone reduces frustration.
Real-Time vs Post-Submit Validation
Real-time validation catches format errors instantly.
Complex validation requiring server checks can wait until submission, but inform users this is happening.
Error Recovery Patterns
Keep valid data when displaying errors so users don’t retype everything.
Show exactly which fields need fixing, preserving correct inputs.
Form Analytics and Testing
You can’t improve what you don’t measure.
Form analytics reveal exactly where users struggle and abandon.
Completion Rate Tracking
Overall completion rate (submissions divided by form views) is your primary metric.
Track this over time and across traffic sources. Paid traffic often shows different completion rates than organic.
Abandonment Rate Analysis
Field-level abandonment shows which specific inputs cause users to quit.
High abandonment at a particular field indicates problems with that question or its position in the flow.
Field-Level Analytics
Time spent per field reveals confusion or difficulty.
Long times suggest unclear labels or complex requirements. Very short times might indicate users are skipping required fields they’ll fail on later.
Time-to-Complete Metrics
Faster completions generally indicate easier forms, but context matters.
Financial applications should take longer than newsletter signups. Compare against your own baseline.
A/B Testing Methodology
Test one variable at a time: button color, field order, label wording, form length.
Split traffic evenly and run tests until you have statistical significance. Small sample sizes produce unreliable results.
Form Accessibility
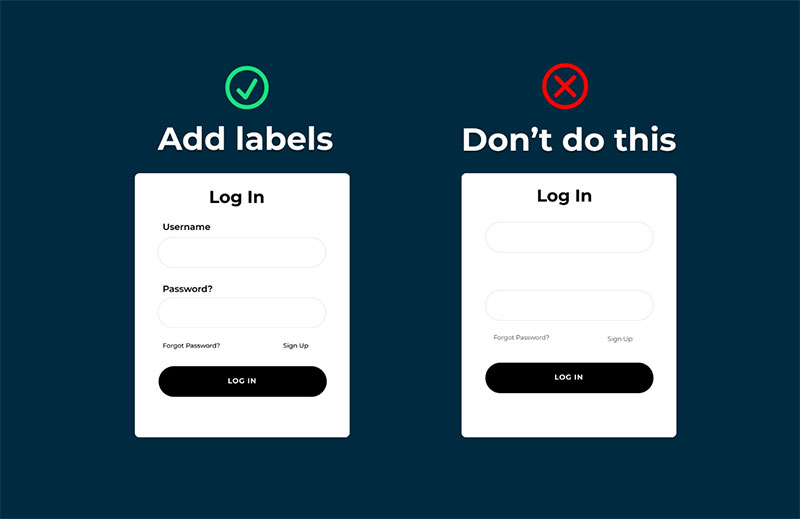
Image source: Alfredo M.
Accessible forms work better for everyone, not just users with disabilities.
Keyboard navigation, screen reader support, and clear focus states improve overall usability.
Screen Reader Compatibility
Every form field needs a proper <label> element associated via the for attribute.
Screen readers can’t interpret placeholder text or adjacent text as labels. Explicit label elements are required.
Keyboard Navigation Support
Users must be able to tab through fields in logical order and submit without using a mouse.
Test your form using only the keyboard. If you can’t complete it that way, neither can many users.
ARIA Labels and Roles
ARIA attributes supplement HTML semantics for complex form interactions.
aria-required="true", aria-invalid="true", and aria-describedby communicate field states to assistive technology.
Color Contrast Requirements
Text and error messages need 4.5:1 contrast ratio against backgrounds minimum.
Red error text on pink backgrounds fails accessibility and looks washed out to users with normal vision too.
Focus Indicators
Visible focus outlines show which field is currently active during keyboard navigation.
Never remove focus indicators without replacing them with equally visible alternatives. Users need to know where they are.
FAQ on How To Optimize Forms For Better Conversions
How many form fields should I use?
Fewer fields always convert better. Aim for 3-5 fields maximum on lead capture forms.
Each additional field reduces completion rates by 5-10%. Only request information you absolutely need immediately.
Should I use multi-step forms or single-page forms?
Single-page forms work best for 6 or fewer fields. Beyond that, multi-step designs reduce cognitive load and feel less overwhelming.
Break complex forms into logical sections with clear progress indicators.
What’s the best position for form labels?
Top-aligned labels convert best across all devices. They’re fastest to scan and work perfectly on mobile screens.
Left-aligned labels work for familiar forms. Never use right-aligned labels.
How do I reduce form abandonment rates?
Remove unnecessary fields, add inline validation, use autofill, and optimize for mobile. Show progress indicators on longer forms.
Fix form abandonment by identifying which specific fields cause users to quit.
What button text converts best?
Action-oriented copy like “Get My Free Guide” or “Start My Trial” outperforms generic “Submit” by 20-30%.
Tell users exactly what happens when they click.
Do security badges really improve conversions?
Yes. Trust signals near submit buttons increase completion rates, especially for forms requesting payment or sensitive data.
Position security badges where users make the final decision to submit.
How important is mobile form optimization?
Critical. Over 60% of submissions happen on mobile devices.
Poor mobile experiences destroy conversion rates through tiny touch targets, wrong keyboard types, and awkward layouts.
Should forms validate in real-time or after submission?
Real-time inline validation catches errors immediately without frustrating users. Validate when users leave a field (onBlur), not on every keystroke.
Post-submit validation forces users to hunt for mistakes.
What makes form error messages effective?
Specific instructions fix problems faster than generic messages. “Password needs 8+ characters, one number, one special character” beats “Invalid password.”
Position errors directly beside problematic fields.
How do I test form performance?
Track completion rates, field-level abandonment, and time-to-complete metrics. Run A/B tests changing one variable at a time.
Tools like heatmaps reveal exactly where users struggle or abandon.
Conclusion
Understanding how to optimize forms for better conversions transforms your user experience and revenue. Every element matters: field reduction, button copy, validation timing, trust signals.
Start with quick wins. Remove unnecessary fields, fix mobile touch targets, add inline validation.
Test changes systematically through A/B testing and form analytics. Track completion rates and field-level abandonment to identify friction points.
Form design isn’t about following every trend. Focus on reducing cognitive load and building trust at decision moments.
Your forms should feel effortless to complete. When users can fly through fields without confusion or frustration, conversion rates follow naturally.
Implement these strategies today and measure the impact.