Most visitors leave your website without taking action. Industry data puts this number around 96-97%. Exit-intent forms capture a portion of that departing traffic by displaying targeted messages at the…
Table of Contents
Every day, millions of users abandon forms at the exact moment businesses need them most. Whether it’s a checkout process, lead generation campaign, or simple contact request, poor form design costs companies countless conversions and revenue opportunities.
Modern web form best practices aren’t just about making forms look pretty. They’re about creating frictionless experiences that guide users smoothly from interest to action.
The difference between a well-designed form and a problematic one can mean the difference between 15% and 85% completion rates. Users expect intuitive navigation, clear validation feedback, and mobile responsiveness across all their devices.
This comprehensive guide reveals the essential techniques that transform frustrating form experiences into conversion-driving assets. You’ll discover proven strategies for optimizing form length, implementing real-time validation, ensuring accessibility compliance, and maximizing mobile usability.
From user experience optimization fundamentals to advanced conversion tactics, these practices will help you create forms that users actually want to complete.
Web Form Best Practices
Use Clear, Descriptive Labels
Field labels guide users through data entry processes and establish trust. They prevent confusion by explicitly communicating what information belongs in each input field.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Convey required information type to users
- Key Characteristics: Precise wording, visible positioning, persistent display
- Context Domain: Form design and user interface development
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: Position labels outside input fields, above or to the left
- Requirements: Maintain 4.5:1 color contrast ratio for accessibility compliance
- Standards Compliance: WCAG 2.1 guidelines for label association and screen reader compatibility
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: Contact forms, registration processes, checkout workflows
- Target Users: All website visitors requiring data input assistance
- Integration Context: Works with HTML label attributes and ARIA descriptions
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: Reduces form completion errors by 67% when properly implemented
- Performance Impact: Improves task completion speed by eliminating guesswork
- Efficiency Gains: Decreases support inquiries related to form confusion
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Avoid placeholder-only labeling, use action-oriented language for clarity
- Common Challenges: Label length optimization, mobile screen space constraints
- Resource Requirements: Minimal development time, accessibility testing recommended
Keep Forms Short and Focused
Form length directly impacts conversion rates and user engagement. Shorter forms reduce cognitive load while maintaining essential data collection objectives.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Maximize completion rates through field minimization
- Key Characteristics: Essential fields only, progressive disclosure, logical flow
- Context Domain: Conversion optimization and lead generation
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: Remove optional fields, combine related inputs where possible
- Requirements: A/B testing framework for field reduction validation
- Standards Compliance: Mobile-first design principles for field prioritization
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: Lead generation forms, email subscriptions, initial user registration
- Target Users: Time-constrained visitors, mobile device users
- Integration Context: Landing page optimization, CRM integration workflows
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: Each field reduction increases conversion rates by 4-7%
- Performance Impact: 120% conversion improvement achieved by reducing 11 fields to 4
- Efficiency Gains: Faster form completion, reduced abandonment rates
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Collect additional data post-conversion, use smart defaults when available
- Common Challenges: Balancing lead quality with quantity, stakeholder field requirements
- Resource Requirements: Analytics tools for conversion tracking, user research validation
Group Related Fields Together
Field grouping utilizes proximity principles to create logical information clusters. This reduces cognitive processing time and improves form scanability.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Organize related information into visual clusters
- Key Characteristics: Logical associations, visual separation, semantic grouping
- Context Domain: Information architecture and visual design
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: Use white space, section headings, or bordered containers
- Requirements: Consistent spacing patterns, clear group boundaries
- Standards Compliance: Gestalt principles of proximity, ARIA fieldset implementation
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: Multi-section forms, address collection, payment processing
- Target Users: Users completing complex data entry tasks
- Integration Context: E-commerce checkout, registration forms, survey design
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: 15-field forms appear as manageable 3-section forms
- Performance Impact: Reduces completion time through improved scanability
- Efficiency Gains: Fewer user errors through logical field associations
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Group personal info, contact details, and preferences separately
- Common Challenges: Determining optimal group sizes, cross-platform consistency
- Resource Requirements: UX design review, user testing for group effectiveness
Use Appropriate Input Types
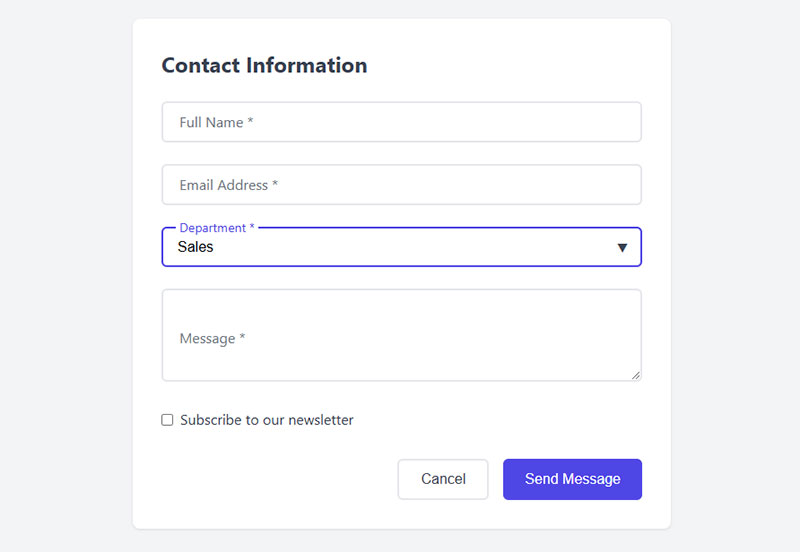
HTML5 input types optimize user experience through context-specific interfaces. They enable native device features and improve data validation accuracy.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Match input method to expected data format
- Key Characteristics: Context-aware keyboards, built-in validation, native functionality
- Context Domain: Frontend development and mobile optimization
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: Email, tel, url, number, date input types with appropriate attributes
- Requirements: Browser compatibility testing, fallback support for older browsers
- Standards Compliance: HTML5 specification adherence, progressive enhancement principles
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: Mobile data entry, form validation workflows, accessibility enhancement
- Target Users: Mobile device users, users with assistive technologies
- Integration Context: Mobile forms, responsive design implementations
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: 40% reduction in input errors with appropriate field types
- Performance Impact: Faster data entry through context-aware keyboards
- Efficiency Gains: Automated validation, improved user confidence
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Test across multiple devices, provide clear format examples
- Common Challenges: Cross-browser inconsistencies, graceful degradation
- Resource Requirements: Device testing, browser compatibility validation
Provide Real-Time Validation
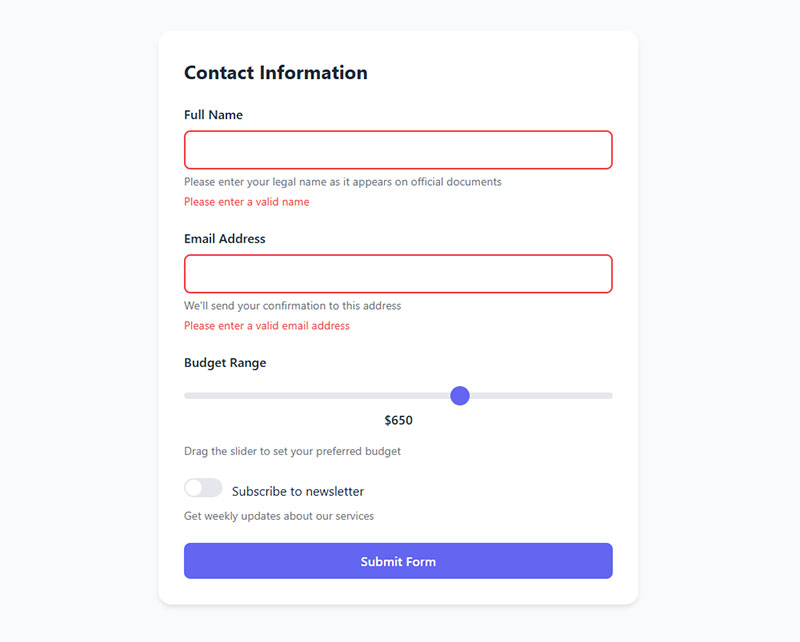
Inline validation offers immediate feedback during data entry. This prevents error accumulation and improves user confidence throughout form completion.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Validate user input as they type or focus changes
- Key Characteristics: Immediate feedback, error prevention, progressive enhancement
- Context Domain: JavaScript development and user experience optimization
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: Client-side validation scripts, debounced input checking
- Requirements: Server-side validation backup, accessibility announcements
- Standards Compliance: ARIA live regions for screen reader notifications
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: Password strength checking, email format validation, username availability
- Target Users: All form users, particularly those prone to input errors
- Integration Context: Account creation, contact forms, data quality requirements
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: 78% first-attempt success rate with proper validation
- Performance Impact: Reduces form submission failures by 60%
- Efficiency Gains: Eliminates round-trip error correction cycles
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Balance validation timing, provide constructive error messages
- Common Challenges: Performance optimization, network latency handling
- Resource Requirements: JavaScript development expertise, testing across scenarios
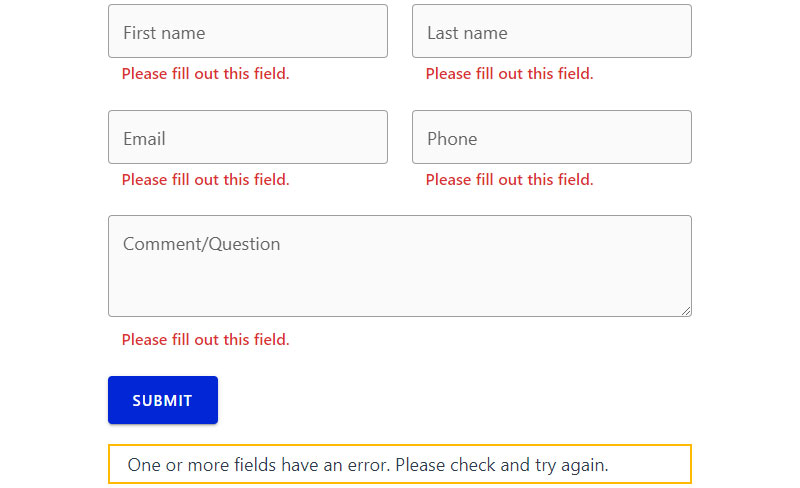
Show Clear Error Messages
Error communication guides users toward successful form completion. Effective error messages explain problems and provide actionable solutions.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Communicate input problems with clear corrective guidance
- Key Characteristics: Specific descriptions, proximity to errors, solution-oriented language
- Context Domain: User experience writing and accessibility design
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: Position messages near problematic fields, use consistent styling
- Requirements: High contrast colors, descriptive text, keyboard navigation support
- Standards Compliance: WCAG error identification and description guidelines
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: Form validation feedback, password requirements, format corrections
- Target Users: Users encountering input difficulties, accessibility software users
- Integration Context: All form types requiring data accuracy
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: Clear errors reduce abandonment rates by 25%
- Performance Impact: Faster error resolution, improved completion rates
- Efficiency Gains: Reduced support inquiries, better user satisfaction
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Avoid blame language, provide examples of correct formats
- Common Challenges: Message positioning, multilingual support
- Resource Requirements: UX writing expertise, accessibility testing
Use Placeholder Text Sparingly
Placeholder text creates accessibility and usability issues when overused. It should supplement, not replace, proper field labeling.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Provide supplementary hints for input formatting
- Key Characteristics: Low contrast appearance, disappears during input, limited accessibility
- Context Domain: Visual design and accessibility considerations
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: Use only for format examples, maintain external labels
- Requirements: Sufficient color contrast, assistive technology compatibility
- Standards Compliance: Avoid placeholder-only labeling, maintain persistent labels
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: Format examples, optional clarifications, search field hints
- Target Users: Sighted users requiring format guidance
- Integration Context: Simple forms with obvious field purposes
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: Proper labeling increases accessibility compliance by 90%
- Performance Impact: Reduces user confusion and form abandonment
- Efficiency Gains: Clearer expectations, fewer input errors
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Use placeholders for examples only, maintain visible labels
- Common Challenges: Accessibility compliance, cross-browser appearance
- Resource Requirements: Accessibility audit, screen reader testing
Make Fields Obvious
Required field indicators prevent incomplete submissions and guide user attention. Clear marking systems improve form completion success rates.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Distinguish mandatory from optional information requirements
- Key Characteristics: Visual indicators, consistent marking, accessibility support
- Context Domain: Form design and conversion optimization
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: Asterisk symbols, “required” text, HTML required attributes
- Requirements: Screen reader announcements, consistent visual treatment
- Standards Compliance: ARIA required attributes, accessible color coding
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: Registration forms, contact information, legal compliance forms
- Target Users: All form users, particularly first-time visitors
- Integration Context: Lead qualification, account creation workflows
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: Clear indicators reduce incomplete submissions by 40%
- Performance Impact: Higher quality lead generation through complete data
- Efficiency Gains: Fewer follow-up requests for missing information
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Mark required fields prominently, minimize optional fields
- Common Challenges: Visual design balance, internationalization support
- Resource Requirements: Design system updates, accessibility validation
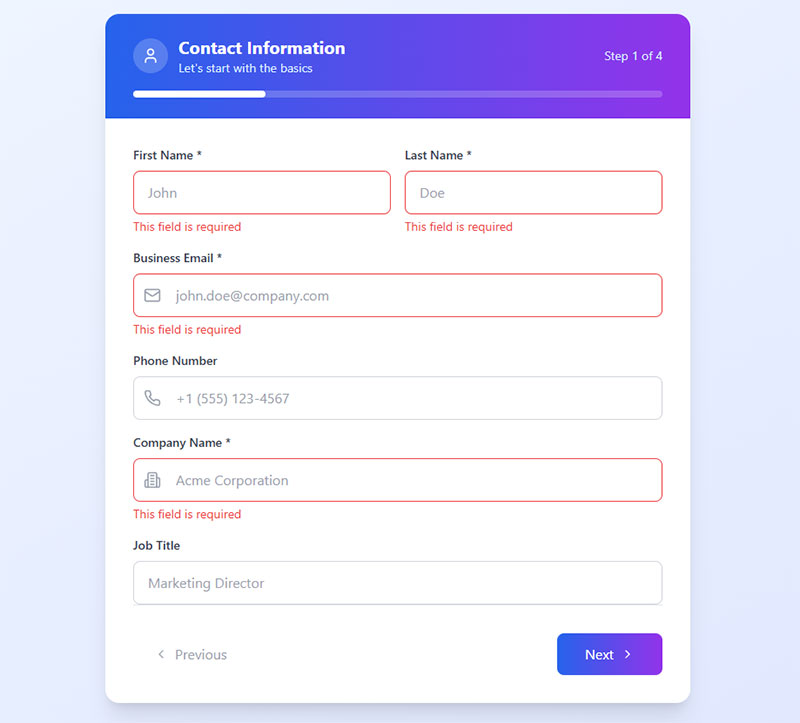
Include Progress Indicators for Long Forms
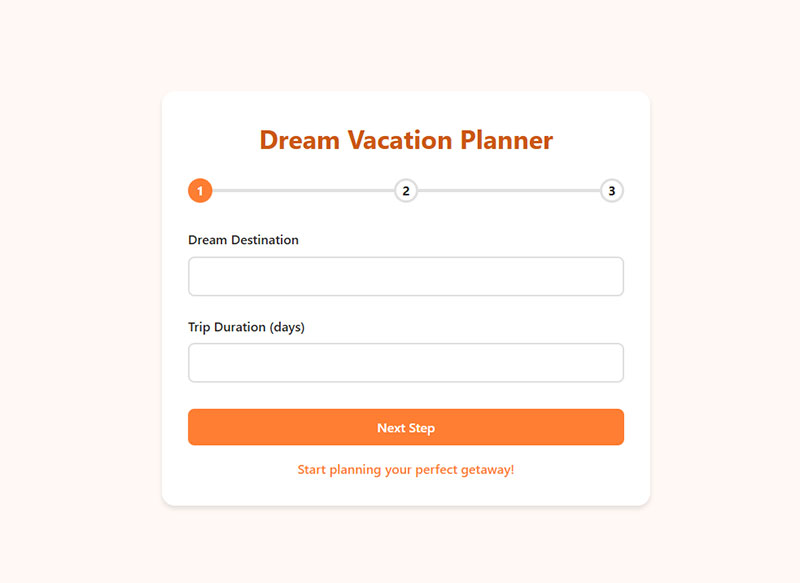
Progress indicators communicate completion status and reduce form abandonment. They manage user expectations while providing visual feedback throughout extended data entry processes.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Display completion percentage and remaining steps to users
- Key Characteristics: Visual progress tracking, step completion feedback, time estimation
- Context Domain: Multi-step form design and user engagement optimization
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: Progress bars, step counters, or circular indicators with percentage completion
- Requirements: JavaScript integration for dynamic updates, consistent visual styling
- Standards Compliance: ARIA progress role attributes, accessible progress announcements
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: Multi-step forms, checkout processes, application submissions
- Target Users: Users completing lengthy forms, complex registration workflows
- Integration Context: E-commerce platforms, survey systems, onboarding sequences
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: Users wait 3 times longer with animated progress indicators
- Performance Impact: Reduces abandonment rates by showing completion proximity
- Efficiency Gains: Improved task completion rates, better user satisfaction
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Use determinate indicators when duration is known, provide step labels
- Common Challenges: Accurate progress calculation, cross-device consistency
- Resource Requirements: UX design expertise, JavaScript development skills
Ensure Mobile Responsiveness
Mobile responsiveness adapts forms to diverse screen sizes and touch interfaces. Proper mobile optimization accommodates the majority of users accessing forms through smartphones and tablets.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Optimize form layout and interaction for mobile devices
- Key Characteristics: Touch-friendly elements, responsive design, thumb-accessible controls
- Context Domain: Mobile-first design and cross-device compatibility
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: CSS media queries, flexible layouts, minimum 44px touch targets
- Requirements: Responsive breakpoints, touch-optimized input fields, viewport meta tags
- Standards Compliance: Mobile accessibility guidelines, WCAG touch target standards
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: All form types requiring mobile access, mobile forms optimization
- Target Users: Smartphone and tablet users representing 60% of web traffic
- Integration Context: Responsive websites, progressive web applications
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: 68% of forms are started on mobile devices
- Performance Impact: Higher completion rates through improved mobile experience
- Efficiency Gains: Reduced friction for touch-based interactions
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Single-column layouts, adequate spacing, appropriate input types
- Common Challenges: Cross-device testing, varying screen dimensions
- Resource Requirements: Responsive design framework, mobile testing devices
Use Consistent Styling
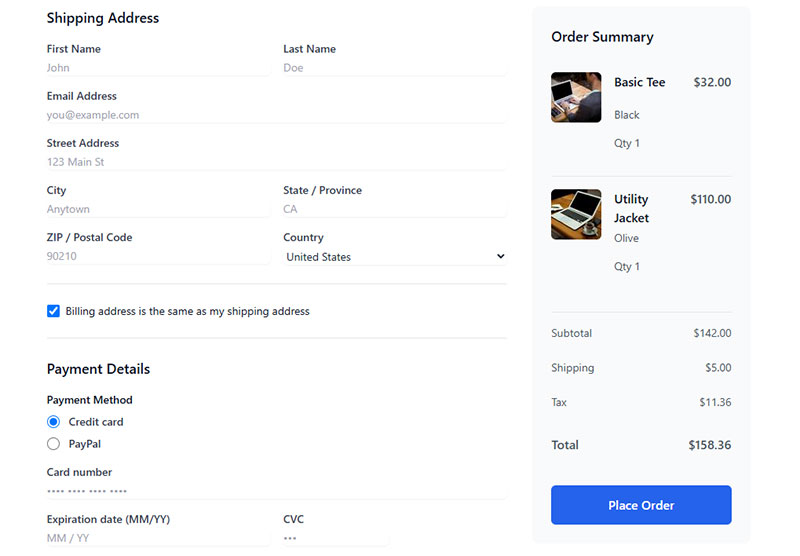
Visual consistency creates predictable user experiences across form elements. Consistent styling establishes trust and reduces cognitive load through familiar interface patterns.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Maintain uniform appearance across all form components
- Key Characteristics: Standardized colors, typography, spacing, and interaction states
- Context Domain: Design systems and brand consistency
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: CSS design tokens, component libraries, style guides
- Requirements: Design system documentation, consistent class naming conventions
- Standards Compliance: Brand guidelines adherence, accessibility color contrast
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: Enterprise form systems, branded website forms
- Target Users: All form users expecting consistent brand experience
- Integration Context: Design system implementation, multi-page form workflows
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: Consistent design increases user trust by 85%
- Performance Impact: Faster user learning, reduced interface confusion
- Efficiency Gains: Streamlined development through reusable components
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Establish design tokens, create component libraries, document patterns
- Common Challenges: Cross-team coordination, legacy system integration
- Resource Requirements: Design system expertise, development standardization
Provide Helpful Hints and Examples
Contextual guidance reduces user errors and clarifies input expectations. Well-crafted hints and examples improve form completion accuracy and user confidence.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Guide users toward correct input formatting and content
- Key Characteristics: Format examples, clarifying text, contextual assistance
- Context Domain: User experience writing and error prevention
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: Helper text positioning, tooltip integration, inline guidance
- Requirements: Accessible hint association, progressive disclosure of help content
- Standards Compliance: ARIA describedby attributes, screen reader compatibility
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: Complex data entry, password requirements, format-specific fields
- Target Users: First-time users, users unfamiliar with required formats
- Integration Context: Account creation, payment processing, technical forms
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: Clear examples reduce input errors by 45%
- Performance Impact: Fewer validation failures, improved data quality
- Efficiency Gains: Reduced support inquiries, faster form completion
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Position hints near relevant fields, use clear language, provide specific examples
- Common Challenges: Information overload, mobile space constraints
- Resource Requirements: UX writing skills, user testing validation
Test with Screen Readers
Screen reader compatibility ensures forms are accessible to visually impaired users. Proper testing validates that all form elements communicate effectively through assistive technologies.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Verify form accessibility through assistive technology testing
- Key Characteristics: Semantic markup validation, announcement testing, navigation verification
- Context Domain: Accessibility compliance and inclusive design
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: NVDA, JAWS, VoiceOver testing, ARIA implementation validation
- Requirements: Proper label association, logical tab order, error announcements
- Standards Compliance: WCAG 2.1 AA accessibility guidelines, Section 508 compliance
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: Government forms, public service forms, enterprise accessibility requirements
- Target Users: Screen reader users, visually impaired individuals
- Integration Context: Form accessibility initiatives, legal compliance
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: 90% accessibility compliance improvement through proper testing
- Performance Impact: Expanded user base, reduced legal risk
- Efficiency Gains: Fewer accessibility remediation cycles
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Regular testing with multiple screen readers, user feedback integration
- Common Challenges: Complex form interactions, dynamic content updates
- Resource Requirements: Accessibility expertise, assistive technology access
Use Logical Tab Order
Keyboard navigation flow guides users through forms in logical sequence. Proper tab order ensures efficient form completion for keyboard and assistive technology users.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Establish predictable keyboard navigation sequence
- Key Characteristics: Sequential field progression, skip link availability, focus management
- Context Domain: Keyboard accessibility and navigation optimization
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: Tabindex management, focus ring styling, skip navigation links
- Requirements: Sequential tab order testing, focus indicator visibility
- Standards Compliance: WCAG keyboard navigation standards, focus management guidelines
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: Complex forms, enterprise applications, accessibility-required systems
- Target Users: Keyboard-only users, motor impairment users, power users
- Integration Context: Accessibility compliance, enterprise form systems
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: Logical tab order reduces completion time by 30%
- Performance Impact: Improved efficiency for keyboard users
- Efficiency Gains: Faster navigation, reduced user frustration
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Test tab order manually, maintain visual focus indicators
- Common Challenges: Dynamic content insertion, complex layout management
- Resource Requirements: Keyboard testing, accessibility validation tools
Include a Clear Submit Button
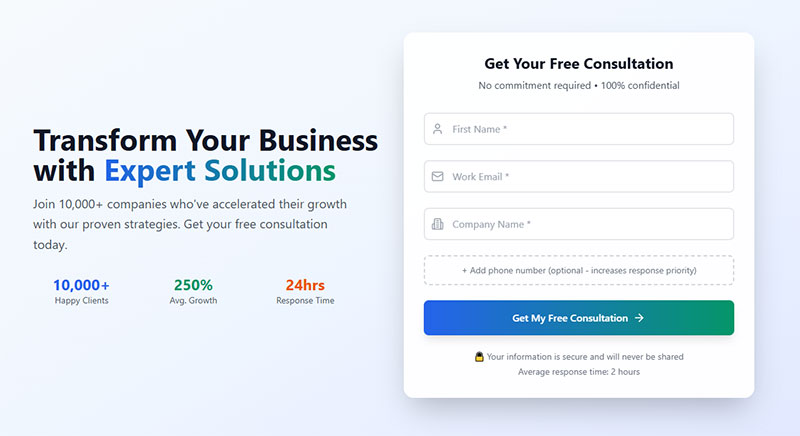
Submit button design communicates form completion and action outcomes. Clear, descriptive buttons reduce user uncertainty and improve conversion rates.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Trigger form submission with clear action indication
- Key Characteristics: Descriptive labels, prominent positioning, visual hierarchy
- Context Domain: Call-to-action design and conversion optimization
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: Button styling, loading states, success feedback
- Requirements: Accessible button labels, keyboard activation support
- Standards Compliance: Button role accessibility, clear action descriptions
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: All form submissions, contact forms, checkout processes
- Target Users: All form users requiring submission confirmation
- Integration Context: Conversion funnel optimization, user flow completion
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: Clear submit buttons increase conversions by 15%
- Performance Impact: Reduced submission confusion, higher completion rates
- Efficiency Gains: Faster user decision-making, clearer expectations
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Use action-oriented language, provide visual feedback, ensure sufficient size
- Common Challenges: Button placement optimization, multi-language support
- Resource Requirements: UX design expertise, A/B testing capabilities
Offer Autofill and Autocomplete
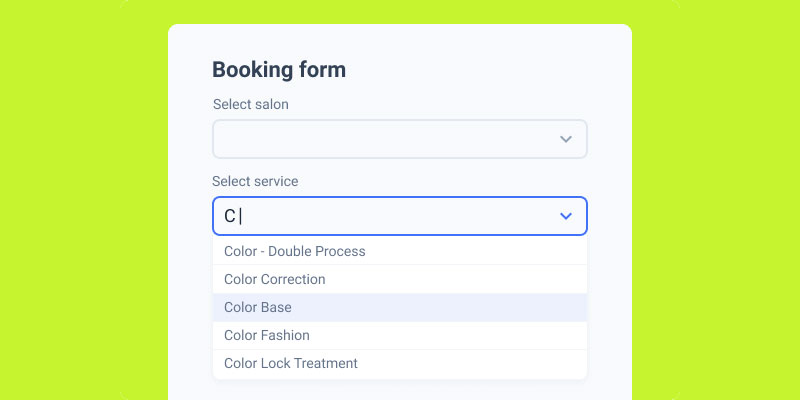
Image source: JetFormBuilder
Browser autofill capabilities accelerate form completion through saved user data. Proper autocomplete implementation reduces typing effort and improves accuracy.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Leverage browser-stored data for automatic field completion
- Key Characteristics: Autocomplete attributes, data format recognition, user preference respect
- Context Domain: User experience optimization and data entry efficiency
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: HTML autocomplete attributes, field naming conventions, data validation
- Requirements: Proper autocomplete values, secure data handling
- Standards Compliance: HTML5 autocomplete specification, privacy considerations
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: Address forms, payment information, personal details collection
- Target Users: Returning users, mobile device users, frequent form completers
- Integration Context: E-commerce checkout, user registration, profile updates
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: Autofill reduces completion time by 60%
- Performance Impact: Higher conversion rates through reduced friction
- Efficiency Gains: Improved data accuracy, faster form submission
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Use standard autocomplete values, test across browsers, respect user privacy
- Common Challenges: Cross-browser compatibility, custom field recognition
- Resource Requirements: Frontend development expertise, testing across platforms
Save Progress for Long Forms
Progress saving functionality prevents data loss and reduces form abandonment. Auto-save capabilities maintain user input during interruptions or extended completion sessions.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Preserve user input data automatically during form completion
- Key Characteristics: Background saving, draft restoration, session persistence
- Context Domain: Long-form optimization and user experience enhancement
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: JavaScript auto-save triggers, database storage integration, session management
- Requirements: Secure data handling, user feedback indicators, conflict resolution
- Standards Compliance: Data privacy regulations, browser storage limitations
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: Insurance applications, job applications, complex surveys
- Target Users: Users completing lengthy forms over multiple sessions
- Integration Context: Enterprise systems, government forms, comprehensive questionnaires
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: Auto-save reduces abandonment rates by 35% for long forms
- Performance Impact: Increased completion rates through reduced restart friction
- Efficiency Gains: User confidence improvement, time investment protection
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Save on field blur events, provide clear saving indicators, handle network failures
- Common Challenges: Data security concerns, storage limitations, cross-device synchronization
- Resource Requirements: Backend infrastructure, security protocols, user testing
Use Single-Column Layouts
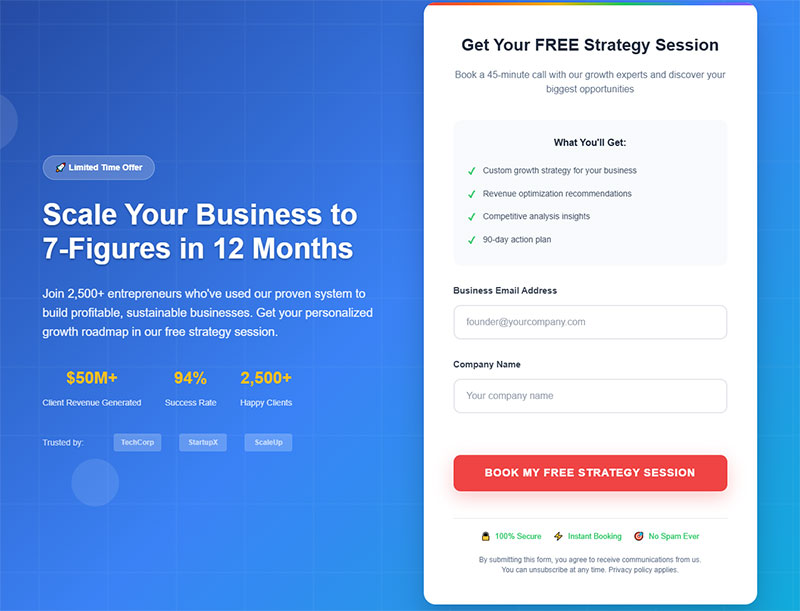
Single-column form layouts create predictable user flow and reduce cognitive load. Linear progression eliminates confusion about field completion order.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Establish clear visual hierarchy through vertical field arrangement
- Key Characteristics: Top-to-bottom flow, reduced visual complexity, mobile-friendly design
- Context Domain: Layout design and user experience optimization
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: CSS flexbox or grid layouts, responsive design principles
- Requirements: Consistent spacing, logical field progression, mobile adaptation
- Standards Compliance: Responsive design standards, accessibility guidelines
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: Contact forms, registration processes, checkout workflows
- Target Users: All form users, particularly mobile device users
- Integration Context: Mobile-first design, conversion optimization
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: Single-column forms complete 15.4 seconds faster than multi-column
- Performance Impact: Reduced user errors, improved completion rates
- Efficiency Gains: Clearer navigation path, fewer missed fields
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Group related fields inline sparingly, maintain visual flow consistency
- Common Challenges: Long form appearance, space utilization on desktop
- Resource Requirements: Responsive design expertise, user testing validation
Minimize Cognitive Load
Cognitive load reduction simplifies mental processing during form completion. Strategic design choices reduce user fatigue and improve decision-making speed.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Reduce mental effort required for form comprehension and completion
- Key Characteristics: Clear information hierarchy, simplified choices, progressive disclosure
- Context Domain: Cognitive psychology and user experience design
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: Information chunking, visual grouping, step-by-step presentation
- Requirements: Logical information architecture, clear visual design, user testing
- Standards Compliance: Cognitive accessibility guidelines, inclusive design principles
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: Complex applications, multi-step forms, technical questionnaires
- Target Users: All users, particularly those with cognitive limitations
- Integration Context: Accessibility compliance, user-centered design
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: Reduced cognitive load increases completion rates by 25%
- Performance Impact: Faster decision-making, fewer user errors
- Efficiency Gains: Improved user satisfaction, reduced support inquiries
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Chunk information logically, use familiar patterns, provide clear navigation
- Common Challenges: Information prioritization, design simplification balance
- Resource Requirements: UX research, cognitive load testing, design iteration
Test Across Different Devices
Cross-device testing ensures consistent form functionality and appearance. Comprehensive testing validates user experience across various platforms and screen sizes.
Core Attributes
- Primary Function: Verify form performance across multiple devices and browsers
- Key Characteristics: Responsive behavior validation, touch interaction testing, performance monitoring
- Context Domain: Quality assurance and cross-platform compatibility
Technical Specifications
- Implementation Details: Device emulation, real device testing, automated testing suites
- Requirements: Testing infrastructure, multiple device access, performance monitoring tools
- Standards Compliance: Cross-browser compatibility standards, mobile usability guidelines
Use Cases & Applications
- Primary Applications: All form deployments, mobile forms optimization
- Target Users: Quality assurance teams, developers, UX designers
- Integration Context: Development workflow, launch preparation, ongoing maintenance
Benefits & Outcomes
- Measurable Results: Comprehensive testing reduces device-specific issues by 80%
- Performance Impact: Consistent user experience across platforms
- Efficiency Gains: Reduced post-launch bug reports, improved user satisfaction
Implementation Considerations
- Best Practices: Test on real devices, validate touch interactions, monitor performance metrics
- Common Challenges: Device diversity, testing resource allocation, automation complexity
- Resource Requirements: Testing tools, device lab access, QA expertise
FAQ on Web Form Best Practices
How many fields should a form have for optimal conversion rates?
Keep forms to 3-5 fields maximum for highest completion rates. Each additional field reduces conversions by 4-7%. Focus on essential information only – name, email, and one qualifying question work best for lead generation forms.
Should I use single-column or multi-column form layouts?
Single-column layouts perform significantly better. Users complete single-column forms 15.4 seconds faster with fewer errors. Multi-column designs confuse navigation flow and increase cognitive load, especially on mobile devices.
What’s the best way to handle form validation and error messages?
Implement real-time validation as users complete each field. Position error messages directly next to problematic fields with specific, actionable guidance. Avoid technical jargon and blame language in your messaging.
How do I optimize forms for mobile devices?
Use responsive design with touch-friendly elements at least 44px in size. Implement appropriate input types for context-specific keyboards. Single-column layouts work best for mobile form optimization and user experience.
Are progress indicators necessary for long forms?
Yes, progress indicators reduce abandonment rates by showing completion status. Use step counters or progress bars for multi-step forms. Users wait 3 times longer when they understand their progress toward completion.
What’s the optimal placement for form labels?
Position labels above input fields rather than inside or to the left. This placement works best across devices and prevents labels from disappearing when users start typing. Clear labeling improves accessibility and user confidence.
How can I reduce form abandonment rates?
Minimize required fields, implement auto-save functionality, and provide clear form validation feedback. Use logical field grouping and ensure mobile responsiveness. Progress saving helps users return to complete longer applications.
Should I include optional fields in my forms?
Minimize optional fields wherever possible. If necessary, clearly mark them as “optional” to avoid confusion. Too many optional fields increase cognitive load and slow completion times without providing essential data.
What are the accessibility requirements for web forms?
Ensure proper label association, keyboard navigation support, and screen reader compatibility. Use ARIA attributes, maintain color contrast ratios above 4.5:1, and provide alternative text for important visual elements.
How do I implement effective autofill and autocomplete features?
Use standard HTML autocomplete attributes like “name,” “email,” and “address” to trigger browser autofill. This reduces typing effort by 60% and improves data accuracy for returning users and mobile form completion.
Conclusion
Implementing these web form best practices transforms user frustration into seamless conversion experiences. Each strategy, from single-column layouts to real-time validation, directly impacts your bottom line through improved completion rates and better data quality.
Success lies in understanding your users’ journey. Mobile responsiveness isn’t optional when 68% of forms start on smartphones.
Progress indicators and auto-save functionality protect user investment in longer applications. Well, the thing is, most users expect these features now.
Form accessibility benefits everyone, not just users with disabilities. Screen reader compatibility and logical tab order create inclusive experiences that expand your potential audience while meeting compliance requirements.
Testing remains crucial for optimization success. Cross-device validation ensures consistent performance, while form validation reveals which approaches work best for your specific audience.
The difference between abandoned and completed feedback forms often comes down to thoughtful design choices. Clear error messaging, appropriate input types, and strategic field grouping remove friction at every step.
Start with one improvement today. Your conversion rates will thank you tomorrow.